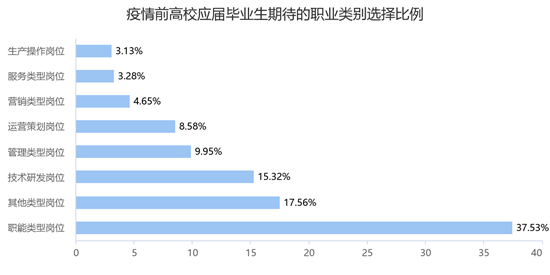
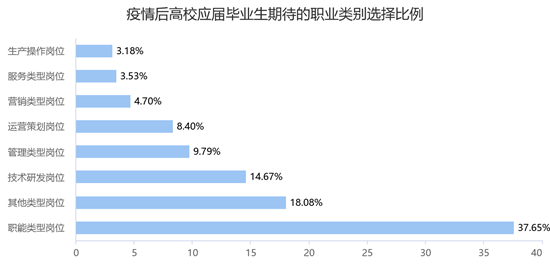
Strict organizational life of the party: an important link in political life and supervision within the party
The Sixth Plenary Session of the 18th CPC Central Committee deliberated and adopted Several Guidelines on the Political Life within the Party under the New Situation (hereinafter referred to as the Guidelines) and the Regulations on Inner-Party Supervision in the Communist Party of China (CPC) (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations). The two documents mentioned "the organizational life of the Party" many times. The main contents of the party’s organizational life include: all party member and cadres, especially senior cadres, must enhance the party’s awareness and always remember that their first identity is party member; Adhere to the system of "three sessions and one lesson"; Adhere to the system of democratic life meeting and organizational life meeting; Adhere to the system of heart-to-heart talk; Adhere to the system of democratic appraisal of party member; Adhere to the reporting system; Leading cadres must strengthen organizational concepts. Strict organizational life of the party has a profound theoretical origin, rich practical connotation and urgent practical needs, which is the key to strengthening party building.
First, the profound theoretical origin
1, the organizational basis of the party’s leadership
For political parties, their leadership is very important. The party’s leadership can be realized, first, by forming a United and strong leadership core; Second, relying on a strong party organization to ensure the implementation of the party’s line, principles and policies.
The formation of a strong Party organization is closely related to a strong contingent of party member cadres. Party constitution stipulated that all party member belonged to a branch, and there was no party member without a branch, so all party member had to lead an organizational life. Specifically, the party’s organizational life is the main way to exercise the party spirit of cadres; The organizational life of the Party is the basic way to educate, manage, supervise and serve the party member team. Implementing the organizational life system and living a good organizational life is very important for implementing the policy of strictly administering the party, enhancing party member’s concept of organizational discipline, and giving play to the role of grassroots party organizations as a fighting fortress and party member’s vanguard and exemplary role. Therefore, strengthening the party’s leadership is inseparable from having a good organizational life.
2. The concentrated expression of the Party’s organizational principles.
Marx and Engels pointed out: "Proletarian political parties must be organized in accordance with the principle of democratic centralism and implement strict organizations and systems." Lenin inherited Marx and Engels’ thought of democratic centralism. In 1902, Lenin wrote "What should I do?"? Expounding the basic principles of the new proletarian political party; In 1904, he further elaborated the idea of establishing a "centralized party" in "Two Steps Back"; From 1905 to 1917, when he led the Russian revolution, he replaced the principle of "centralism" with the principle of "democratic centralism"; Subsequently, this principle was adhered to and developed in the process of creating a new type of proletarian party. On the practical level, Lenin’s thought of democratic centralism is embodied in the party’s congress system, collective leadership system, minority obeying majority system, reporting system and so on. Among them, some contents are closely related to the party’s organizational life, and some contents themselves belong to the party’s organizational life system.
The Communist Party of China (CPC) inherited and developed the organizational principle of democratic centralism. Democratic centralism is the fundamental organizational principle of Marxist political parties, and organizational life is an important embodiment of Marxist political parties following democratic centralism.
3, the inevitable requirement of the party organization structure.
Marx and Engels clearly demanded in the Constitution of the Communist League that the organizational system of the Party should be established from the bottom up from the branch to the Central Committee, so that the Party can become a unified system. In the process of the development of proletarian political parties, Lenin gradually made it clear that the party should set up grass-roots party organizations according to regions and production units, deeply root the party’s grass-roots organizations in its own class, and make every social grass-roots party organization such as factories, schools, organs and villages become the basis of the party’s work and all its combat effectiveness. In the history of the Communist Party of China (CPC), the four party constitution have stipulated that in rural areas, factories, railways, mines, barracks, schools and other grassroots units; Since the "Three Bays Adaptation", the Party has established the principle of "the branch is built on the company" in the people’s army. This organizational form effectively combines the party’s organizational construction with the armed struggle, adapts to the needs of the revolutionary struggle at that time, and gives full play to the role of the party branch as a fighting fortress and party member’s vanguard and exemplary role; After the Eighth National Congress, the basic organizations were renamed as grass-roots organizations.
In the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, party constitution stipulated that organizations should be divided into central, local and grass-roots units. Among them, it is stipulated that the party’s grass-roots organizations are "the fighting bastion of the party in social grass-roots organizations and the basis of all the party’s work and combat effectiveness." It can be seen that the organizational life of the party is mostly carried out in the grassroots organizations of the party, and the operation of the grassroots organizations of the party basically depends on the organizational life of the party.
Second, rich practical connotation
1, the historical continuation of the party’s internal laws and regulations
The organizational life of the party has experienced a historical process from initial understanding to gradual improvement and standardization, and finally formed a series of important systems of inner-party life. During the revolutionary war years, party leaders attached great importance to the party’s organizational life. In 1980, the Fifth Plenary Session of the Eleventh Central Committee of the Communist Party of China adopted "Several Guidelines on Political Life within the Party". Its main contents and principles are still applicable. For example, it is stipulated that "every party member, regardless of his position, must join an organization of the Party and participate in organizational life". Since the 12th National Congress of party constitution, party constitution has stipulated that party member should lead a party organization life. Article 8 of party constitution of the 18th National Congress clearly stipulates: "Every party member, regardless of his position, must join a branch, group or other specific organization of the Party, participate in the organizational life of the Party, and accept the supervision of the masses inside and outside the Party." "party member leading cadres must also participate in the democratic life meeting of party committees and leading groups. There is no special party member who does not participate in the party’s organizational life and does not accept the supervision of the masses inside and outside the party. " These are the historical experiences summed up by the Party in practice and exploration, and are the important institutional guarantee for the Party to manage the Party strictly.
2. Spiritual legacy of the older generation of revolutionaries.
The Communist Party of China (CPC) people have always attached importance to the party’s organizational life, and the party’s leaders set an example. In 1944, as the chairman of the CPC Central Committee, Comrade Mao Zedong abided by the party’s organizational life system, and volunteered to report his personal thoughts at the party group meeting, hoping that the party group leader would supervise him. During the Anti-Japanese War, Zhu De, as the commander-in-chief of the Eighth Route Army, took the lead in organizing life every time. A party group meeting in response to Chairman Mao’s call to "do it yourself and overcome difficulties" did not inform Comrade Zhu De to attend. Comrade Zhu De found the leader of the party group and stressed: "Chairman Mao called on us to do it ourselves and overcome difficulties. I am also involved in such a big event — Share. " He also said kindly, "Everyone in our Party is an ordinary party member, and there can be no special party member in the Party. In the future, I will be notified to attend such meetings. " Comrade Chen Yun and party member, among the secretaries, guards and other staff members, formed a party group, with the chief bodyguard as the leader of the party group. Chen Yun couldn’t attend, so he took the initiative to ask for leave and even wrote a letter in person. Deng Xiaoping’s comeback in 1973 began with Zhou Enlai’s proposal that the Political Bureau should make a "Decision on Restoring Comrade Deng Xiaoping’s Party Organizational Life and Vice Premier the State Council’s post". This decision was sent to county and regimental party committees to inform the whole party and the people of the whole country, and Mao Zedong gave instructions to "agree". Thus, the revolutionaries of the older generation have fulfilled the Party’s requirements and made party member, especially party member, a leader,带头参加党的组织生活。
3、以最高领袖同志为核心的党中央率先垂范
以最高领袖同志为核心的党中央对参加党的组织生活高度重视。“中共中央总书记、国家主席、中央军委主席最高领袖以普通党员身份参加了所在的中办机关党委直属党支部的组织生活会,与支部成员一起交流并发表了重要讲话。他说,‘参加支部生活会,我们都是平等的、普通的一员,这也是作为共产党员应尽的义务。共产党员这个称号,是一个组织称号,在组织里的人,就要过组织生活,不参加组织活动的人,也就脱离党了。’”最高领袖总书记作为党的领导核心仍能坚持党的组织生活制度,对全体党员而言,既是以身作则、以上率下,也是巨大的振奋和鼓舞。
Third, urgent practical requirements
1, the importance of the party’s organizational life itself
The party’s organizational life plays a very important role. First, standardize the operation of party organizations and consolidate the organizational foundation of the party. The important way of inner-party life is the organizational life of the party. If the operation of the party organization is more standardized and the organizational foundation is more solid, it is necessary to strictly control the organizational life of the party. The second is to go deep into the grassroots to obtain first-hand materials for investigation and research. General Secretary of the Supreme Leader pointed out: "Investigation and research are the foundation of seeking something and the way to accomplish it. Without investigation, there is no right to speak, and there is no decision-making power. " Leading cadres can communicate with grassroots cadres and grassroots party member and get first-hand information through democratic life meetings, organization life meetings and heart-to-heart talks. Third, the means of connecting emotions to enhance the cohesion and centripetal force of grass-roots organizations. No matter leading cadres or ordinary party member, they all live in the same party branch, which helps to form a good atmosphere. Therefore, where there is party member, there must be a Party organization, and where there is a Party organization, there must be a sound organizational life.
2. The importance of the party’s organizational life to the political life within the party.
The "Guidelines" clearly pointed out: "The party must manage the party from the political life within the party, and strictly manage the party from the political life within the party." At the same time, it is pointed out: "The party’s organizational life is an important content and carrier of the political life within the party, and it is an important form for the party organization to supervise party member’s education management." This points out the important position of the party’s organizational life in the party’s management of the party and strict management of the party.
The Code stipulates and puts forward clear requirements from 12 aspects: strengthening ideals and beliefs, adhering to the Party’s basic line, resolutely safeguarding the authority of the Party Central Committee, strictly observing the Party’s political discipline, maintaining the flesh-and-blood ties between the Party and the people, adhering to the principle of democratic centralism, promoting inner-party democracy and safeguarding party member’s rights, adhering to the correct orientation of selecting and employing people, strictly enforcing the Party’s organizational life system, carrying out criticism and self-criticism, strengthening the restriction and supervision of power operation, and maintaining a clean and honest political nature. Among them, the ninth part of the special train is "Strict Party’s organizational life system". It is pointed out that "the organizational life of the Party is an important content and carrier of the political life within the Party, and it is also an important form for the Party organizations to supervise party member’s education management. We must adhere to the various systems of the party’s organizational life, innovate ways and means, and enhance the vitality of the party’s organizational life. " It is mentioned in the guidelines that "all party member and cadres, especially senior cadres, must enhance the party’s awareness and always remember that their first identity is party member"; "Insist on ‘ Three sessions and one lesson ’ System "; "Adhere to the system of democratic life meeting and organizational life meeting"; "Insist on the system of heart-to-heart talk"; "Insist on democratic appraisal of party member"; "Leading cadres must strengthen their organizational concepts,Major issues and personal matters in the work must be reported to the organization in accordance with the regulations and procedures, and the requirements should be made in advance to the organization for instructions before leaving the post or work place. The party’s organizational life is an important part of the party’s political life, so we must adhere to the party’s organizational life system and improve the political life within the party.
3, the importance of the party’s organizational life for inner-party supervision.
The "Regulations" pointed out: "In the supervision system, establish and improve the inner-party supervision system with unified leadership of the CPC Central Committee, comprehensive supervision by party committees (party groups), special supervision by discipline inspection organs, functional supervision by party departments, daily supervision by party grass-roots organizations and democratic supervision by party member."
In the inner-party supervision system, many supervision methods are closely related to the party’s organizational life. First, at the supervision level of the party’s central organization, Article 14 states: "members of the Political Bureau of the Communist Party of China Central Committee should strictly implement the eight central regulations, consciously participate in the life of dual organizations, and truthfully report personal important matters to the Party Central Committee." Dual organizational life refers to members of the Political Bureau of the Communist Party of China Central Committee’s participation in the Political Bureau of the Central Committee and the Standing Committee on the one hand; On the one hand, it is also incorporated into grass-roots branches. Second, at the level of supervision by party committees (leading groups), Article 20 stipulates that "the party’s organizational life system should be strictly enforced, democratic life meetings should be regularized, and important or universal issues should be convened in time. Democratic life will focus on solving outstanding problems. At the meeting, leading cadres should clearly and thoroughly explain the problems reflected by the masses, patrol feedback and organization of interviews and letters, carry out criticism and self-criticism, put forward rectification measures, and accept organizational supervision. Party organizations at higher levels should strengthen the guidance and supervision of the democratic life meetings of lower-level leading bodies and improve the quality of democratic life meetings. " Third, at the level of the Party’s grass-roots organizations and party member’s supervision, Article 35 stipulates that "the Party’s grass-roots organizations play the role of fighting bastions and perform their supervisory duties". Among them, "Strictly organize the Party’s life, carry out criticism and self-criticism, supervise party member to earnestly fulfill its obligations, and ensure that party member’s rights are not infringed" ranks as the first duty. Thus, the party’s organizational life is an important part of inner-party supervision, and it is in the central organization, party committees (party groups)Grass-roots organizations and party member’s supervision level are all reflected, so we must strengthen inner-party supervision in the organizational life of the Party.
Fourth, the principle of strictly organizing life
1, comply with the rules and regulations and outstanding problem orientation.
Party constitution stipulated: "Every party member, regardless of his position, must join a branch, group or other specific organization of the party, participate in the party’s organizational activities, and accept the supervision of the masses inside and outside the party." Strict organizational life of the Party needs to be based on party constitution and the Party’s rules and regulations. At the same time, we need to pay attention to the problems and shortcomings of organizational life. At present, the party’s organizational life is generally standardized and orderly, but there are also some problems. Just as in the recent Interpretation (1) of the Supervision Department of the Central Commission for Discipline Inspection, it is proposed that "what problems are solved, what problems are highlighted, and what problems are focused on, so as to enhance the pertinence of reality". To highlight the problem orientation in strict organizational life is to pay attention to the problems in organizational life during the inspection, the problems in the party organization, the problems in party member around us, and party member’s own problems.
2. Senior cadres should set an example and actively practice in grassroots party member.
The General Secretary of the Supreme Leader stressed that "especially the members of the central leadership must set an example, strictly abide by the party’s political discipline and rules, adhere to Do not forget your initiative mind, move on, take the lead in setting an example and set an example for the whole party and society." "About focusing on senior cadres. Strengthening and standardizing political life within the party and strengthening inner-party supervision are the requirements and common tasks of the whole party. At the same time, both the draft guidelines and the draft regulations emphasize the focus on senior cadres. The main consideration is that to strengthen party building, we must do a good job of leading cadres, especially senior cadres, and it is the key to do a good job of the members of the Central Committee, the Political Bureau of the Central Committee and The Politburo Standing Committee (PSC). " This clearly shows the requirements for senior cadres. At the same time, party member and cadres need to actively practice. It is necessary to do a good job in learning at different levels, and in accordance with the requirements of the Central Committee, "learning the spirit of the Sixth Plenary Session of the Eighteenth Central Committee of the Communist Party of China is the key task of the theoretical armed work of the whole party, and it is included in ‘ Two studies and one doing ’ Study and educate, formulate careful study plans and programs, and promote the broad masses of party member and cadres to comprehensively and accurately grasp the spirit of the plenary session. "
3. Inherit the essence of tradition and innovative ways and means.
General Secretary of the Supreme Leader pointed out: "The most striking feature of the two drafts is the organic unity of inheritance and innovation, which not only deeply summarizes the experience and lessons of our party in strengthening its own construction, but also inherits and carries forward the institutional provisions and fine traditions formed by our party in the long-term practice, and comprehensively summarizes the vivid practice of the CPC Central Committee in promoting the comprehensive and strict management of the party since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, and collects the theoretical and practical innovations of the comprehensive and strict management of the party." Therefore, on the one hand, we should continue the traditional ways, and adhere to the traditional systems of "three meetings and one lesson", organizing life meetings, heart-to-heart talks, ideological reports, democratic appraisal of party member and party member’s party spirit, democratic life meetings for leading cadres in party member and dual organization life meetings for leading cadres in party member. On the other hand, we should innovate ways and means. For example, combine the party’s organizational life with the actual business of the unit to discuss major issues of the unit; For another example, using the Party’s organizational life, party member was organized to watch the recent hit documentary "Always on the Road", and the interpretation of the spirit of the Sixth Plenary Session of the Eighteenth Central Committee was studied by the online feature film, so that the Party’s line, principles and policies were put into the mind through modern carriers and methods. (Author: Sun Qiaojing, Department of CPC History, Renmin University of China)