As we all know, infection is almost inevitable in plasma cell disorders (PCD). Although infection is not the diagnostic standard of PCD, it is a common complication of most patients, and it is also an important cause of morbidity and mortality of patients, especially the elderly and immunocompromised patients. In addition, the increasing use of immune-based therapeutic drugs in multiple myeloma may also have a negative impact on infection epidemiology and clinical outcome.
According to statistics, the risk of infection in patients with multiple myeloma is 7 times higher than that in the general population; 10% patients died within 60 days after diagnosis, of which 45% were attributed to infection, and most of them occurred in elderly patients; 17% of multiple myeloma deaths are attributed to infection, and before the first-line treatment, the highest death rate was caused by infection (46%)1.
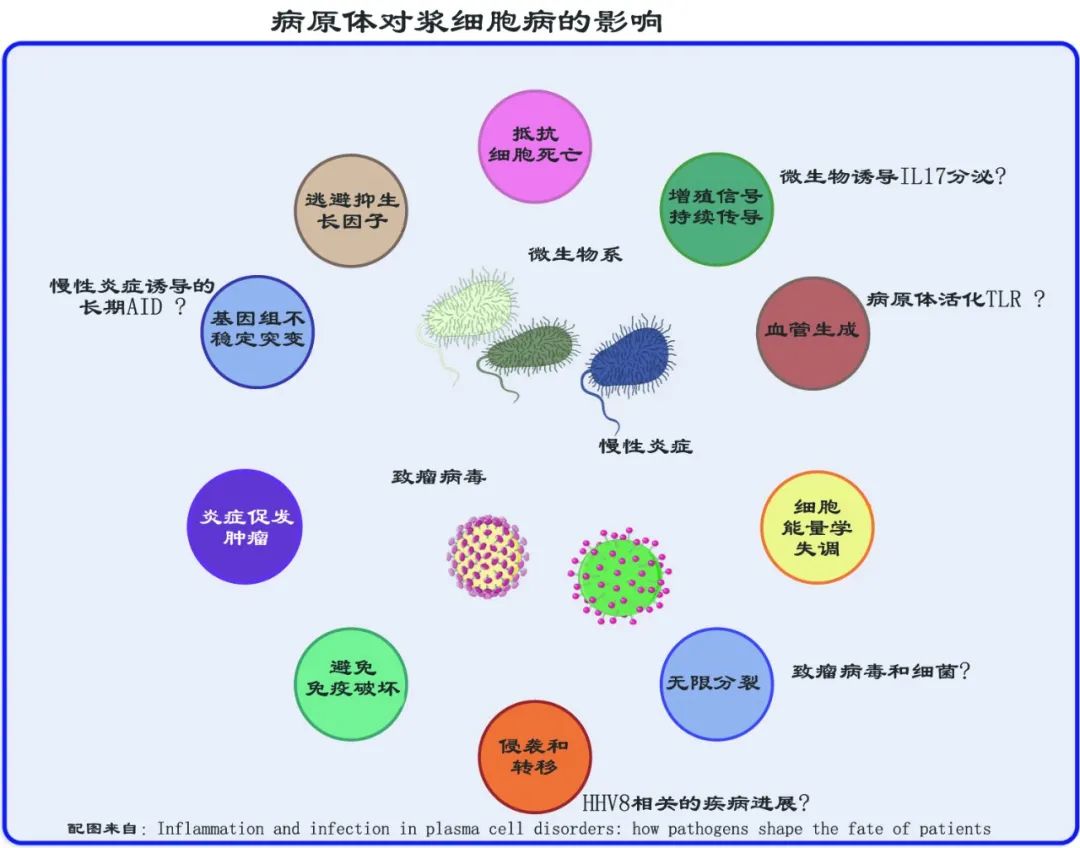
In addition, infection, inflammation and pathogens also play an important role in the pathogenesis of plasma cell disease. Infectious cancer factors can be divided into direct carcinogens and indirect carcinogens. The former expresses viral oncogenes that directly contribute to carcinogenic transformation, while the latter causes cancer through chronic inflammation and acquired driven mutation. The mechanism of pathogen carcinogenesis includes pathogen as the direct carcinogen of PCD (oncogenic virus assists the occurrence of immunosuppressive cancers, such as Kaposi sarcoma and HHV8) and pathogen as the indirect carcinogen of PCD (chronic inflammation can enhance cell proliferation, and abnormal immune response to self-protein or infectious pathogens increases the risk of gene change and subsequent malignant transformation into dominant MM, Long-term antigen stimulation may also promote the genomic instability of MM by combining cytidine deaminase) and pathogens as regulators of PCD immune monitoring (Th17 cells secrete inflammatory cytokines, and promote the growth of plasma cells through IL-6-STAT3 signaling pathway and local activation of eosinophils; Intestinal flora may affect the response and toxicity of immunotherapy, and the principle is that immunosuppressants and broad-spectrum antibiotics can significantly change the composition of microbial flora.
As mentioned earlier, infection is still the main cause of morbidity and mortality of patients with multiple myeloma due to the cumulative effect of disease, treatment and host-related factors. In view of the cumulative risk of infection in the whole course of disease, it is very important to prevent infection. At present, the best prevention strategies include vaccination against common pathogens, antibacterial prevention, infection management and immunoglobulin replacement for a small number of patients. But in general, there is no universally accepted infection prevention guideline for multiple myeloma.
In view of this, the International Myeloma Association convened 36 experts from all over the world to jointly review the existing literature and guidelines, and solve the problems related to the infection risk and prevention of infectious complications of multiple myeloma under the emerging treatment background, including providing personalized infection treatment strategies for MM and providing suggestions for preventing infectious complications. The consensus statement was published in Lancet Haematology in February.


Panel1: Summary of key points and key suggestions for preventing infection in patients with multiple myeloma
Infection is still the main cause of death in patients with multiple myeloma. Risk factors include immunosuppression, treatment, age and complications (such as renal failure and weakness) of multiple myeloma.
The period with the highest risk of infection is the first 3 months after diagnosis and when treating relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.
Patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma are more likely to prevent potential infections (such as Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae).
Most infections in patients with multiple myeloma are caused by viruses and bacteria: bacterial infections are most often manifested as pneumonia and bacteremia, while viral infections are usually manifested as seasonal viruses, especially influenza and herpes zoster.
If the risk of infection increases, levofloxacin can be considered for prevention (NCCN 2A level). Patients with seropositive herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus (such as detection) can be given acyclovir for prevention. It is recommended that patients who receive proteasome inhibitors or targeted monoclonal antibodies, especially CD38 targeted monoclonal antibodies, use acyclovir for prevention (NCCN level 1). Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole can be reserve for patients at risk of pneumocystis Yersinia pneumonia, such as patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma or patients receiving large doses of dexamethasone (for example, ≥40 mg/ day, 4 days a week). For patients with sulfur allergy, alternative drugs such as dapsone (NCCN 2A grade) can be considered.
It is suggested that patients with multiple myeloma should be vaccinated with inactivated influenza vaccine (preferably with two doses of influenza vaccine, regardless of age) and inactivated streptococcus pneumoniae vaccine (PCV13) every year, and then with PPSV23(NCCN 2A level) every five years.
Only patients with multiple myeloma are recommended to be vaccinated with inactivated vaccine.
The ability to produce protective response after immunization depends on the immunosuppressive status of patients (such as disease load, remission status, cumulative immunosuppression of anti-tumor treatment) and vaccination time.
Conventional chemotherapy can significantly impair the response of patients with multiple myeloma to vaccination.
Vaccination at the early stage of the disease (such as MGUS or SMM), before the start of treatment or when it reaches remission can get the best protection.
Lenalidomide monotherapy can improve the response of patients with multiple myeloma to vaccination, provided that dexamethasone is not given at the same time. At present, the immune response after receiving new drugs (such as monoclonal antibody, panobinostat and Cellini) has not been determined.
After autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, patients with multiple myeloma may lose immunity to the pathogens they were vaccinated against, and these patients should be vaccinated again 6-24 months after HSCT. The data show that it is safe and effective to inoculate recombinant herpes zoster vaccine after autologous HSCT. Therefore, it is recommended to inoculate recombinant herpes zoster vaccine after autologous HSCT (NCCN level 1).
It is suggested that the recombinant herpes zoster vaccine should be extended to all patients with multiple myeloma. It is suggested to continue to use varicella-zoster vaccine for prevention according to the indications, regardless of the vaccination status (NCCN 2b level).
It is suggested that patients with multiple myeloma should use passive immunization after being exposed to hepatitis A, chickenpox or measles (NCCN 2b).
It is suggested that close contacts of patients with multiple myeloma should be routinely vaccinated with inactivated vaccine, and patients should avoid close contact with live vaccine vaccinators as much as possible (NCCN 2A level).
Encourage the medical care and family members of patients with multiple myeloma to receive all designated immunization, especially seasonal influenza virus (NCCN 2A level).
Intravenous immunoglobulin is suitable for specific situations, such as life-threatening infection and IgG concentration below 400mg/dL with recurrent infection (NCCN 2A level).
For patients with multiple myeloma who go to infected epidemic areas, it is recommended to receive vaccines and antibacterial prevention at the destination, and consult infectious disease experts or medical institutions at the destination.
Risk factors of infection in patients with multiple myeloma

Disease factors
Plasma cell diseases can increase the susceptibility of patients to viral and bacterial infections. The increased risk of infection in newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma is caused by the common global immune insufficiency paralysis in this patient, including the dysfunction of B cells in hypogammaglobulinemia, the destruction of global T cell diversity, and the significant changes in the functional activities of dendritic cells, natural killer cells and alternative complement pathways.
Although rare at the time of seeing a doctor, neutropenia associated with bone marrow infiltration can also increase this risk. Of course, other related complications such as renal failure are also risk factors. The highest risk of infection is in the first 3 months after diagnosis and when treating recurrent or refractory multiple myeloma.
Therapeutic factors

Basic principles of treatment and infection of multiple myeloma

The main therapeutic drugs for multiple myeloma are shown in Table 1. These treatments significantly improved the patient’s outcome, and transformed myeloma from a rapidly fatal disease to a chronic disease with multiple recurrences (usually successfully saved), but it also led to cumulative immunosuppression and increased risk of infection. For example, CD4 cell count drops sharply with the increase of chemotherapy cycle, which is closely related to opportunistic infection. Even so, the deep and lasting remission achieved by the combined regimen will generally lead to the reversal of immunosuppression and improvement of outcome.
The immune status of patients with multiple myeloma is related to many factors, including the disease state and treatment stage (such as induction, remission vs first relapse vs relapse or refractory to multiple types and drugs), the degree of previous treatment (such as single drug vs multiline) and the intensity of treatment (such as triple induction vs autologous HSCT myeloablative regimen). In addition, continuous treatment can cause mild persistent immune suppression, which leads to an increase in the risk of infection. Immunomarkers can be used to determine whether there is cumulative immunosuppression.
glucocorticoid
The cumulative dose of dexamethasone is an independent risk factor for infection, both during induction and at the time of recurrence. In addition, high-dose accumulation of glucocorticoids (for example, dexamethasone ≥40 mg/ day, 4 days per week) will increase the risk of opportunistic infections, including pneumocystis Yersinia.
Cytotoxic chemotherapy
Conventional chemotherapy drugs, such as cyclophosphamide, etoposide, cisplatin, anthracyclines, melphalan and bendamustine, can enhance the susceptibility of patients with multiple myeloma to infection by inducing neutropenia, T cell dysfunction and mucosal damage.
Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
High-dose melphalan combined with autologous HSCT (the standard treatment of multiple myeloma) can cause severe neutropenia and gastrointestinal mucositis, thus making patients susceptible to severe infections (mainly bacterial infections). Long-term T cell immune deficiency after implantation is rare, but it can increase the risk of virus infection and pneumocystis acquisition and reactivation.
Proteasome inhibitor
Bortezomib can deplete T cells and impair viral antigen presentation, and the incidence of reactivation of varicella-zoster virus is relatively high in seropositive patients, so the preventive treatment of acyclovir is very important (NCCN grade 1). Caffezomib and Isazomib are also powerful immunosuppressants and have the same risk of viral infection. EMN guidelines recommend stopping antiviral preventive treatment 6 weeks after stopping PI. The authors suggest that the duration of prevention should be adjusted according to the immunosuppressive status of patients and whether other immunosuppressants (such as glucocorticoids or monoclonal antibodies) that increase the risk of varicella-zoster virus are given subsequently.
immunomodulator
Lenalidomide and pomadomide can cause neutropenia, especially when combined with monoclonal antibodies. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor does not seem to reduce the risk of infection during lenalidomide treatment, but it can be used intermittently to fight chronic neutropenia. Thalidomide alone will not increase the risk of infection in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma unless it is combined with other immunosuppressants (especially dexamethasone).
monoclonal antibody
Monoclonal antibodies are associated with severe lymphopenia, pneumonia, reactivation of viral infection (especially varicella zoster virus) and opportunistic infection (especially in patients with intensive pretreatment). Clinical neutropenia may occur when monoclonal antibody is used in combination with lenalidomide or pomadumide, so the dosage needs to be adjusted. The neutropenia rate of CD38-targeted monoclonal antibody was higher than that of elotuzumab.
Selinexor in Cellini.
May lead to neutropenia-related infections.
New immune drugs
Methods of targeting mature antigens of B cells, such as cell therapy (e.g. chimeric antigen receptor T cells), bispecific T cell adapters and antibody drug conjugates (e.g. belanatmab mafodotin), will all lead to immunosuppression because of targeting antibody-producing B cells and plasma cells. Therefore, patients with multiple myeloma who receive this treatment may need immunoglobulin replacement therapy. In addition, these treatments can lead to neutropenia and bone marrow suppression, and in some cases preventive use of antibiotics, antiviral coverage and antifungal coverage are needed.
Inhibition of bone resorption therapy
Most patients with multiple myeloma will use anti-bone resorption therapy to prevent bone diseases. Rarely infected mandible and maxilla lead to jaw necrosis. Poor oral hygiene, poor denture fit, advanced periodontal disease and recent alveolar surgery are the risk factors. If infection occurs in the case of jaw necrosis, it is suggested to start using broad-spectrum antibiotics active against anaerobic bacteria, including actinomycetes spp46 and drug-resistant Bacteroides fragilis, such as clindamycin, carbapenems or β -lactamases or β -lactamase inhibitors. If the response to antibiotics is slow or unsatisfactory, or osteomyelitis is suspected, it is suggested to biopsy the lesion through staining and culture. Limited debridement may be required at this time; However, for refractory multiple myeloma, surgical resection should be reserve.
Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty
Vertebral kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty are generally well tolerated and are essential to control the pain associated with multiple myeloma of the vertebral body. In rare cases, spondylitis caused by Gram-positive bacteria (such as Staphylococcus aureus) can develop and evolve into paravertebral abscess. It is suggested that antibacterial prevention should be used 24 hours before operation and during operation when planning such operations for patients with high risk of infection.
Host factor
Multiple myeloma mainly affects elderly patients with aging immune system (age ≥65 years old), whose antibody responses to pneumococcal and influenza vaccines are reduced, and the possibility of clinically significant complications is increased.
What factors can predict early and severe infection in MM patients?
A considerable number of newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma will die prematurely before they can benefit from effective treatment, and the main reason is infection. Predictors of early and severe infection in newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma include high tumor load (ISS score II–III), abnormal increase of IDH, poor physical fitness and renal insufficiency.
The prognosis model developed in 2018 divided patients into high-risk (infection rate was 24% during tertiary treatment) and low-risk (infection rate was 7%). In addition, men and high tumor load (ISS scores II-III and IDH increased) were risk factors for pneumonia, while high tumor load (ISS scores II-III) and increased serum creatinine concentration could independently predict the risk of sepsis.
Immune reconstruction after successful treatment
Effective control of multiple myeloma can usually improve immunity. Immune reconstruction after autologous HSCT may provide an opportunity window for vaccination that may produce protective response.
Infection spectrum of patients with multiple myeloma
With the introduction of new therapy, the types, severity and time of infection complications in patients with multiple myeloma have changed, and the complications mostly occur in the first few months of induction therapy and reach the peak in 4-6 months. The pathogens are mainly Gram-positive bacteria (such as coagulase-negative Staphylococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Enterococcus faecalis) and Gram-negative bacteria (such as Haemophilus influenzae and Escherichia coli). In addition, tracheobronchitis and pneumonia caused by respiratory viruses (such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus) are also common.
Infection can reach its peak again during the treatment of recurrent diseases, so the immunity of patients with multiple myeloma is seriously damaged. In addition, the uncommon infections in patients with multiple myeloma include invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and viral infections, such as cytomegalovirus, hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) and parvovirus B19, and tuberculosis and other opportunistic infections are also rare.
Prevention and treatment strategies of multiple myeloma infection
The key to reduce the burden of infection complications in patients with multiple myeloma is to carry out comprehensive staging in diagnosis and recurrence, so as to adjust individualized treatment strategies according to risks. Staging includes collecting clinical history (especially vaccination and past infection), checking physical health and evaluating the functional status of patients over 65 years old (that is, healthy, moderately healthy or weak).
It is suggested to optimize the dose intensity in patients with high risk of severe infection (that is, high disease load or increased IDH) and clinically significant complications (especially renal insufficiency). In addition, it is suggested that the preventive strategies of immunosuppression state should be considered when using various previous treatment lines to treat recurrent patients, including vaccination against common pathogens (Table 2), paying attention to the time of vaccination (panel 2), and educating patients and nurses to take measures to reduce exposure to potential pathogen sources, including traveling (panel 3). In addition, it is suggested to carry out risk-adaptive antibacterial prevention in a small number of patients (Table 3), and consider immunoglobulin replacement and possible myeloid growth factor support. Careful monitoring during high immunosuppression therapy and after autologous HSCT may predict the risk and type of infection.



Panel 2: Vaccination Opportunity of Inactivated Vaccine for Multiple Myeloma Patients
MGUS, SMM or asymptomatic MM
These patients can respond to immunization.
Vaccination may be more effective for the following patients: MGUS with low concentration of M protein and SMM may need to be vaccinated repeatedly to be effective.
MM in need of treatment
MM status is related to insufficient immune response, and the precautions are as follows:
Inoculate as soon as possible
Vaccinate patients 14 days before starting treatment (preferred)
In partial remission (especially immune reconstruction)
Good remission is usually associated with immune reconstitution, with unaffected immunoglobulin returning to normal.
Inhibition of uninvolved immunoglobulin is a risk factor for insufficient response to repeated vaccination.
When the immunomodulator is used alone or in combination with proteasome inhibitor,
Immunomodulators alone or in combination with proteasome inhibitors are associated with increased possibility of serological response.
Maintenance therapy with a single immunomodulator (lenalidomide) can enhance immunity to some pathogens, but it will not enhance immunity when combined with dexamethasone.
Non-influenza respiratory tract infection in influenza season
Avoid immunization for the time being, because the response to the vaccine may not be sufficient, and the overall infection risk of patients with active multiple myeloma may increase.
During routine chemotherapy
Avoid vaccination until the disease is controlled, because the response of cancer patients may be insufficient, and the higher the load of multiple myeloma, the higher the risk of infection.
When high-dose myeloablative therapy combined with autologous HSCT
Avoid vaccination before autologous HSCT, because the response to the vaccine cannot be sufficient.
Patients were replanted 6-12 months after autologous HSCT, because patients would have severe humoral and cell-mediated immune deficiency after autologous HSCT, but the immune reconstruction was rapid.
The recovery of ?CD4 cell count is a marker of immune recovery.
Recurrent/Refractory Multiple Myeloma
Avoid immunization during active diseases, because the response to vaccines cannot be sufficient, especially in patients who have received several lines of treatment in the past.
Cumulative immunosuppression after extensive treatment can increase the net state of immunosuppression and the risk of severe infection.
The possibility of vaccine response decreases in descending order. There are no vaccine response data for monoclonal antibodies, Papi and Cellini.

Panel 3: Travel Notes for Patients with Multiple Myeloma
To evaluate the immune status, it is not recommended for patients with severe immune dysfunction to travel to potentially severe infection epidemic areas.
Update the patient’s immune status and verify the drug.
Patients are advised to use general protective measures, insect repellents, mosquito nets and protective clothing to minimize the risk of mosquito bite infection (such as malaria, dengue virus, Chikungunya fever, Zika virus and West Nile encephalitis) and ticks (such as Borrelia Lyme disease, tick-borne encephalitis and relapsing fever).
Provide relevant country-specific and region-specific vaccination according to the risk, including drugs against Neisseria meningitidis, hepatitis A virus and hepatitis B virus, and poliovirus.
Provide antibacterial prevention in specific countries and regions, including malaria and tuberculosis.
Provide antibiotics (such as fluoroquinolones or macrolides) that can be used for self-administration for persistent diarrhea with fever (> 48h), and actively encourage patients to seek medical treatment when the situation occurs.
Immunoglobulin seronegative and high-risk groups of hepatitis A virus infection should consider hepatitis A immunoglobulin, including those who go to areas where hepatitis A virus is prevalent.
Educate patients and nursing staff as follows:
Understand specific risk areas, focusing on malaria and tuberculosis.
Avoid raw food, eat peelable fruits and vegetables, prevent travelers from diarrhea, and only drink bottled or boiled drinks.
Avoid bad cooking of meat
Avoid close contact or long-term contact with crowded tuberculosis patients and closed environments (such as hospitals or clinics); If you plan to travel, check for tuberculosis (skin or blood) before leaving and after returning home.
Avoid activities that increase the risk of fungal infection (such as digging) to prevent endemic fungal pneumonia.
Detection of infection
Fever is regarded as the most important sign of infection in patients with multiple myeloma. Patients without fever should be highly suspicious, especially those receiving corticosteroids. It is suggested to obtain the vaccination history, past infection, virus serum status, disease status, recent treatment and related complications of patients to determine possible pathogenic pathogens, and of course, local epidemiology should also be considered.
It is suggested that patients with febrile neutropenia and patients with infection should start empirical broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment when they are diagnosed and tested. In addition, it is suggested to choose drugs active against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Gram-negative pathogens, especially Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibacterials should be recommended according to clinical, imaging and microbiological results.
Diagnostic tests of infection include complete blood cell count and classification, liver and kidney function examination, electrolyte examination and microscopic examination or culture of blood and other parts according to clinical indications. It is also recommended to obtain rapid pneumococcal antigen detection in urine, blood and cerebrospinal fluid samples when there are indications.
For patients with respiratory manifestations, it is suggested to scan the chest and sinuses with CT, collect nasopharyngeal samples for respiratory pathogens detection, microscopic examination or culture of respiratory secretions, and detect Legionella urine antigen. For persistent fever with lung infiltration for more than 3-4 days, it is suggested to consider bronchoscopy combined with bronchoalveolar lavage or bronchial biopsy to determine conditional pathogens. Fungal infection markers, such as galactomannan and β-glucan, can be used when there are clinical indications.
For abdominal symptoms and diarrhea, it is recommended to start using broad-spectrum antibiotics immediately. In addition, it is suggested that the infection of Clostridium difficile can be confirmed by stool samples. If it can be confirmed, it is suggested to add oral vancomycin because its activity is better than metronidazole. There is evidence that fidamycin is at least as effective as oral vancomycin for the confirmed Clostridium difficile infection, and may be related to the lower risk of recurrent infection, especially when it is used as extended pulse therapy for 25 days. Empirical treatment should be considered when severe colitis exists, especially when the infection index of Clostridium difficile is suspected to be high, until the diagnosis and detection results are obtained.
It is suggested that the abdomen and pelvis should be scanned by CT to find severe focal signs and symptoms. According to local epidemiology, it is suggested to obtain PCR of fecal culture and intestinal pathogens, as well as other tests of intestinal parasites (such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium).
If the fever persists and the cause is unknown, further diagnostic imaging examination is suggested to determine the existence, location and degree of infection. Once an infection cause is ruled out, other causes of fever diseases related to multiple myeloma should be considered, such as tumor fever, venous thromboembolism, adrenal insufficiency or implantation syndrome synchronized with bone marrow recovery after autologous HSCT. Other patients with stable clinical signs should consider non-infectious causes if their fever persists after the best exploration and antibacterial treatment. Tumor fever should be considered when the concentration of serum LDH and other markers of multiple myeloma in blood and urine increases abnormally. Fever associated with venous thromboembolism should be excluded by Doppler or ultrasound examination of limbs, ventilation or perfusion scanning or CT scanning, especially in patients at risk of venous thromboembolism, such as patients receiving immunomodulatory imide drugs or recombinant erythropoietin, patients with restraint (due to fracture or spinal cord compression) or patients with other known risk factors. Patients with fever of unknown origin should always consider drug-induced fever. Fever under the background of new immunization strategy may also be a symptom of cytokine release syndrome and should be treated appropriately.
Consider infection treatment according to the disease state and treatment period.
Newly diagnosed MM
Because pneumococcus is a common pathogen when multiple myeloma is first diagnosed, it is suggested that pneumococcus vaccine should be inoculated as soon as possible (Table 2), and if there is fever or other infection, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs active against pneumococcus should be given.
Induction treatment period of newly diagnosed MM
A considerable proportion of newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma died in the first few months after diagnosis, mainly due to infection complications, so we should actively manage them by starting fast active drugs and treating complications related to multiple myeloma, such as renal failure. Levofloxacin can be considered for antibacterial prevention in the first 3 months of treatment, especially in patients with high risk of early infection, although its benefits are still unknown under the current triple and quadruple treatment strategies (NCCN 2A level). The benefits of using fluoroquinolones (such as levofloxacin) should be weighed, because these drugs are rarely associated with tendinopathy with rupture, especially Achilles tendon. The risk factors of tendinopathy include old age (> 60 years old), concomitant use of corticosteroids and renal insufficiency. Table 3 lists other antibacterial prevention suggestions according to disease stages and anti-tumor treatment types. The use of quinolones should be considered according to the degree and duration of neutropenia.
Autologous HSCT consolidation period
Multiple myeloma patients with autologous HSCT are at risk of serious infection (mainly bacterial infection), so it is suggested to use antibacterial drugs to prevent it, and the immune deficiency after autologous HSCT may lead to clinically significant infection. It is recommended to monitor infection and prevent pneumocystis carinii for 3 months and prevent herpes simplex virus or varicella zoster virus for 1 year (NCCN 2A level) according to global guidelines. Antibacterial prevention is not a routine practice in all transplant centers around the world. Although its use reduces the incidence of fever and bloodstream infection, it does not translate into a reduction in mortality. Antibacterial prevention also needs to consider the risk of drug resistance.
Maintenance treatment period
Severe infection during maintenance treatment is mainly due to neutropenia, but the risk is low and the mortality rate is lower than 1%.
Treatment period of recurrent MM
Patients with recurrent and refractory myeloma are at high risk of life-threatening broad-spectrum pathogen infection, including bacterial and viral infections (such as herpes simplex virus or varicella-zoster virus, cytomegalovirus, HBV and HCV). Fungal pneumonia, including invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and pneumocystis, may also occur.
Infection screening
For relapsed/refractory MM with positive cytomegalovirus serum reaction, it is suggested to detect HBV (cytomegalovirus antigenemia or quantitative PCR) or circulating HBV DNA(NCCN 2B grade) before starting treatment. Patients with high suspicion suggest that serum Aspergillus galactomannan antigen should be tested before symptoms appear to detect invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. The effect of serum (1,3)-β-D- glucan on invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is not clear, but it may be a useful auxiliary means to diagnose pneumocystis disease.
According to the patient’s serum status, HBV reactivation can lead to severe complications and death in patients with multiple myeloma, and usually occurs after autologous HSCT. In addition, HBV reactivation was rarely observed after treatment with CD38-targeted monoclonal antibody. It is suggested that patients should be managed according to their HBV serum status and the type and duration of immunosuppressive therapy (Table 3). It is suggested that antiviral prevention should be used for patients with HBV reactivation or high risk of disease, or early preemptive treatment should be used for patients with low risk. Only in the presence of clinically relevant diseases (such as cytopenia and cytomegalovirus diseases) can cytomegalovirus disease be treated.
The effect of chronic HCV on the course of multiple myeloma is not very clear, but it is known that it will be reactivated after chemotherapy, and it may be necessary to reduce or stop taking drugs, but acute liver failure or death is not the outcome of chronic HCV infection. It is suggested that HCV serum status should be evaluated when multiple myeloma is diagnosed, and interferon α-free treatment schemes, such as direct antiviral drugs (such as sofebuvir, cimetivir and redipavir), should be used during the whole treatment period, and serum alanine aminotransferase and HCV viral load should be closely monitored.
Before stem cell mobilization, it is very important to monitor HCV viral load and treat infection. Chronic HCV infection may cause three-line hemocytopenia and lead to poor mobilization. Cancer patients may rarely lose HCV seropositivity, so it is suggested to measure HCV viral load when the patient’s serum status is unknown. It is recommended to seek help from infectious disease experts in complex situations.
vaccine
General principle of multiple myeloma vaccine
Although the response to vaccination is usually very small, partial protection may still reduce the infection rate and hospitalization rate, but it should also be noted that the duration of benefit is unknown and may vary with vaccination time. Although the safety of most vaccines has not been tested in patients with multiple myeloma, inactivated vaccines such as influenza and pneumococcal vaccines are safe. Patients with multiple myeloma strongly recommend vaccination against Streptococcus pneumoniae and seasonal influenza virus, as well as vaccines necessary for local epidemiology (such as HBV). Splenectomy patients are also vaccinated against Haemophilus influenzae.
It is suggested that patients with multiple myeloma should be vaccinated with pneumococcal vaccine, including one dose of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and another dose of polysaccharide vaccine (PPS V23) at least 8 weeks later. If the patient has been vaccinated with PPSV23 before, it is recommended to be vaccinated with PCV13(NCCN 2A grade; Table 2). The protective titer of pneumococcus is unknown, which may vary according to serotype. If a breakthrough pneumococcal infection occurs after vaccination, it is suggested to try to identify the serotype of the strain to report the non-response to the vaccine (if possible). The purpose of serotype identification is to determine whether this serotype is included in the PCV13 vaccine-for example, patients vaccinated with PCV7 or PCV10. In this case, consider vaccination with PCV13 vaccine.
Because the antibody response of pneumococcal vaccine may not be ideal, it may be useful to prolong antibiotic prevention in patients with recurrent pneumococcal infection and patients with invasive pneumococcal disease. Although penicillin G is the standard treatment, antibiotics based on strain sensitivity and local drug resistance patterns that have caused invasive pneumococcal diseases in the past can be used. Fluoroquinolones (such as levofloxacin), azithromycin or second-generation penicillin or cephalosporin are reasonable substitutes (NCCN 2B grade). (panel 1)。
Vaccination against seasonal influenza virus is necessary because cancer patients are at increased risk of infection and death. It is suggested that patients with multiple myeloma be vaccinated with two doses of inactivated tetravalent influenza vaccine instead of standard vaccine, regardless of age (NCCN 2A level). The initial dose should be given as early as possible in the flu season, and the second high-dose booster vaccination should be carried out one month later. For patients with inactivated influenza vaccine in serious adverse events, two doses of recombination vaccines can be considered.
It is generally recommended to vaccinate against HBV, especially for patients with high risk of virus infection (NCCN 2A level). Other potentially useful vaccines for patients with multiple myeloma include vaccines against Neisseria meningitidis, tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis, and inactivated poliovirus vaccines.
Because of the increased risk of reactivation of varicella-zoster virus during the treatment of multiple myeloma, vaccination should be considered to reduce the risk of infection and post-herpetic neuralgia. It is suggested that patients with multiple myeloma should be vaccinated with recombinant herpes zoster vaccine instead of live herpes zoster vaccine, because it is safe (that is, non-live vaccine) and can provide higher and longer-lasting prevention of herpes zoster, thus preventing post-herpetic neuralgia (NCCN grade 1). However, even after vaccination, patients treated with proteasome inhibitors or CD38-targeted monoclonal antibodies should continue to receive acyclovir preventive treatment, because the degree of protection provided by vaccination is difficult to assess (NCCN 2A level). Specifically, patients with multiple myeloma have different immune responses and are highly dependent on their immune status, so they cannot be prevented by vaccination alone. For patients who have been vaccinated with live herpes zoster vaccine in the past, it is recommended to vaccinate with 2 doses of recombinant herpes zoster vaccine at least 8 weeks after vaccination.
Generally speaking, due to the lack of safety or efficacy data, live vaccines are not recommended for patients with multiple myeloma. For patients with MGUS and SMM, considering their relatively healthy immune system, we can consider vaccination with live vaccine. Measles, mumps and rubella vaccines and live herpes zoster vaccine have been used after HSCT. If patients are in remission, they can be considered for use under certain circumstances.
Vaccination of non-immune close contacts
Patients with multiple myeloma, especially those receiving treatment, may not be able to produce immune response to pathogens, and close contacts vaccinated with inactivated vaccine may also provide group immunity for patients. Therefore, according to vaccination history, age and exposure history, it is suggested that non-immune close contacts should be vaccinated with vaccines that are usually suitable for individuals with normal immune function, and it should be emphasized that inactivated vaccines (NCCN 2A level) should be used. Encourage the medical care and family members of patients with multiple myeloma to receive all designated immunization, especially seasonal influenza virus immunization.
Immunoglobulin substitution
Immunoglobulin replacement can be administered intravenously, subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended for patients with plateau multiple myeloma who have hypogammaglobulinemia and recurrent bacterial infection and have no response to pneumococcal immunization. However, immunoglobulin substitution supports the scarcity of contemporary data, high cost, limited availability and the possibility of complications (including acute renal failure and cardiovascular events). It is suggested that replacement therapy should be limited to patients with serum IgG concentration below 400 mg/dL and severe and recurrent infection caused by capsular bacteria (or other pathogens reasonably thought to be caused by hypogammaglobulinemia), even with antibacterial prevention and immunization (NCCN 2A level).
Another potential consideration includes patients with insufficient antibody production, especially pneumococcal vaccine. Using immunoglobulin replacement therapy can only benefit patients infected with pathogens, which may respond according to the specific antibody titer against the target pathogen in intravenous immunoglobulin preparation; For example, it is used for infection caused by severe parvovirus B19 in patients with multiple myeloma.
When planning to use intravenous immunoglobulin, it is necessary to evaluate the patient’s immune status and infection history (especially recurrent infection), and carry out laboratory examination of immune parameters (including specific antibody response) to determine the patients who can benefit from early intravenous immunoglobulin intervention.
Immunoglobulin infusion is usually well tolerated, and most reactions are frequency dependent. But serious complications may also occur, including acute renal failure and rare cardiovascular events (such as myocardial infarction, stroke or venous thromboembolism). It is suggested to give standard preoperative medication to reduce the severity of infusion-related reactions, and to replenish water before infusion, especially in patients with hyperviscosity, risk factors of renal complications and receiving sucrose-containing preparations. It is suggested that intravenous immunoglobulin therapy should be started at a slow rate of 0.01 mL/kg/min and gradually increased to a maximum rate of 0.08 mL/kg/min according to the tolerance. If the serum IgA concentration cannot be detected, it is recommended to use intravenous immunoglobulin to remove IgA.
Post-exposure prevention of immunosuppressed MM patients
Immunoglobulin prevention may have protective effect on patients with multiple myeloma who are immunosuppressed after exposure to chickenpox, herpes zoster and hepatitis A (NCCN 2B grade). Serious diseases after exposure to herpes zoster, especially chickenpox, are very high, so it is very important to determine the risk level. The infectious stage begins 1-2 days before the rash occurs, so patients can appear several days after exposure. Except the recipients of autologous HSCT, all immunocompromised patients with a history of chickenpox infection can be considered immune. For patients with no history of varicella infection, risk assessment includes determining the susceptibility and exposure duration of patients. Risk factors include recent use of proteasome inhibitors, previous vaccination against varicella, severe immunosuppression, and close face-to-face or indoor contact for more than 1 hour. Post-exposure prevention depends on varicella-zoster immunoglobulin, ideally within 96 hours after exposure, but the benefit can be extended to 10 days. If immunoglobulin of varicella-zoster is not easily available, it is recommended to use acyclovir after exposure. The typical incubation period of chickenpox is 14-16 days. However, since the immunoglobulin of varicella zoster may prolong the incubation period, it is recommended to monitor the evidence of varicella for up to 28 days after exposure in the recipients of this therapy.
For patients with multiple myeloma who travel to areas where hepatitis A virus is prevalent, it is recommended to give 0.02 mL/kg of hepatitis A immunoglobulin within 2 weeks of travel, and give the initial dose of hepatitis A vaccine. It is recommended to give a dose of hepatitis A immunoglobulin to patients with known exposure.
For patients who have not been vaccinated against HBV or whose anti-HBV titer is less than 10 IU/L after vaccination, it is suggested to use tenofovir or entecavir for prevention to avoid the need for HBV immunoglobulin.
Patients may occasionally need tetanus immunoglobulin 138 or human rabies immunoglobulin 139 after specific high-risk exposure. For patients at risk of respiratory syncytial virus infection in virus season, it is not recommended to use intravenous immunoglobulin or palizumab, that is, humanized monoclonal antibody against respiratory syncytial virus F glycoprotein.
Myeloid growth factor
Prophylactic granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor (granulocyte colony stimulating factor is better) is recommended for patients without fever, and the risk of fever and neutropenia in these patients is at least 20%(NCCN 2A grade). The decision on whether to use granulocyte colony stimulating factor to prevent treatment delay (such as treatment delay related to lenalidomide) should be considered individually. Chronic neutropenia occasionally needs the support of growth factors.
references
1. Jessica Caro, Marc Braunstein, Louis Williams, et al. Inflammation and infection in plasma cell disorders: how pathogens shape the fate of patients. Leukemia . 2022 Feb 2. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01506-9.
2. Noopur S Raje, Elias Anaissie,Shaji K Kumar, et al.Consensus guidelines and recommendations for infection prevention in multiple myeloma: a report from the International Myeloma Working Group. Lancet Haematol . 2022 Feb; 9(2):e143-e161. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00283-0