Has the employment expectation of college graduates in China changed before and after the epidemic?

On September 26th, Luoyang City, Henan Province, the 8th large and medium-sized cities jointly recruited college graduates (autumn). The Luoyang special session of Henan Station roving job fair was held in Henan University of Science and Technology, and job seekers were looking for jobs on the spot. It is reported that this is the largest on-site job fair held in Luoyang this year. Photo courtesy of vision china
Employment and epidemic situation make our social pressure intertwined, and all walks of life pay unprecedented attention to the employment of college graduates under the impact of epidemic situation. Before and after the epidemic, did the college graduates’ employment expectation place, employment expectation salary, employment expectation unit nature, employment expectation industry and employment expectation occupation category change?
The research group of "Comprehensive Investigation on the Employment Situation of College Graduates in China during the Epidemic Period" led by the author, the key research base of humanities and social sciences of the Ministry of Education, tried to answer the above questions.
The research group cooperated with Changsha Yunyan Technology Co., Ltd. and Beijing Xinjincheng Data Technology Co., Ltd. in the important graduation season of college graduates — — From April to June, 2020, a random sampling survey was conducted among college graduates from 34 provincial administrative regions in China. A total of 13,767 students were collected and 13,738 were valid. This survey includes the age group of 18 to 50 years old, and 87% of the sample size is concentrated in the age group of 21-24 years old. There are 1660 college graduates, 11395 undergraduate graduates, and 683 graduate students with master’s degree or above respectively. The universities where the sample data of fresh graduates are located include first-class universities (2.10%), first-class universities with various disciplines (2.30%), national key universities (2.50%), provincial key universities (19.00%), ordinary undergraduate universities (68.90%) and higher vocational colleges (5.10%).
The focus of employment has generally shifted to second-tier cities as the most potential winners.
Generally speaking, there is little difference in the ideal employment expectation of college graduates in China before and after the COVID-19 epidemic, but the internal structure fluctuates greatly, and the focus of employment expectation moves down slightly. Before the epidemic, the proportion of employment expectations was second-tier cities (31.42%), new first-tier cities (29.15%), prefecture-level cities (18.07%), first-tier cities (14.11%), county towns (5.67%), towns (1.09%) and villages (0.20%). After the epidemic, the selection proportion of employment expectation is second-tier cities (32.13%), new first-tier cities (28.39%), prefecture-level cities (19.66%), first-tier cities (11.56%), county towns (6.50%), towns (1.09%) and villages (0.17%).
Before and after the epidemic, the proportion of choosing second-tier cities, prefecture-level cities and county towns as ideal employment expectation places increased slightly, and the rising proportion was prefecture-level cities, county towns and second-tier cities from high to low. The proportion of first-tier cities, new first-tier cities and villages declined slightly, while the proportion of villages and towns was flat. It can be seen that before and after the epidemic, the focus of employment expectation of college graduates in China shifted slightly, and the ratio of outflow and inflow of employment expectation was relatively highest in first-tier cities and prefecture-level cities.
The research group further studied the internal changes of employment expectation choices of college graduates, and found that the consistent choices of employment expectation before and after the epidemic were: second-tier cities, prefecture-level cities, new first-tier cities, county towns, first-tier cities, towns and villages. Among them, the relatively highest change rate is the fresh graduates who chose villages before the epidemic, and 65.22% of them changed after the epidemic. Among those who changed, 46.67% chose second-tier cities and 20.00% chose county towns. Secondly, fresh graduates from Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan were selected before the epidemic, and 37.50% of them chose new first-tier cities after the epidemic.
Among the cities with employment expectation above prefecture level, the change rate from high to low is first-tier cities, new first-tier cities, prefecture-level cities and second-tier cities, among which the first-tier cities have the highest flow, the new first-tier cities have the highest flow, the second-tier cities have the highest flow, the second-tier cities have the highest flow, and the prefecture-level cities have the highest flow, and the second-tier cities and counties have the highest flow.
Generally speaking, second-tier cities are the employment expectation places with the smallest fluctuation, the strongest stability, the least outflow and the relatively high inflow willingness among the employment expectation choices of college graduates before and after the epidemic. It can be seen that the epidemic has shifted the overall employment focus of college graduates, and at the same time, second-tier cities have become the most potential winners in the fluctuation of college graduates’ desire to choose employment places.
The expected salary of employment has not changed much, and more than 80% is concentrated in 3001-8000 yuan.
Before the epidemic, the expected salary of college graduates in China was 1,000-3,000 yuan, 3,001-5,000 yuan, 5,001-8,000 yuan, 8,001-10,000 yuan, 10,001-15,000 yuan and 15,000 yuan, and the proportions were 4.48%, 40.11% and 41.77% respectively. It can be seen that there is little difference in the overall change of expected salary, and more than 80% of fresh graduates expect salary between 3001-8000 yuan.
The research group conducted a study on the internal structural changes in the choice of employment expectation salary for college graduates, and found that the stability of employment expectation salary for graduates before and after the epidemic was more than 15,000 yuan (90.37%), 3,001-5,000 yuan (82.05%), 5,001-8,000 yuan (75.76%) and 8,001-10,000 yuan (61. The proportion of graduates who expected to earn more than 15,000 yuan before the epidemic was the most stable, and the consistency reached more than 90%. Nearly 40% of the graduates whose expected salary before the epidemic was 8,001-15,000 yuan and 1,000-3,000 yuan changed after the epidemic, with the highest change ratio and the worst stability. Among them, the most concentrated fluctuation range is the graduates whose expected salary is 1,000-3,000 yuan. Although 38.79% of the graduates in this group chose another salary after the epidemic, as high as 83.42% of the other candidates chose 3,001-5,000 yuan, with the highest degree of concentration.
More than 80% of the fresh graduates’ expected salary is 3,001-8,000 yuan, so it is necessary to focus on the fluctuation of expected salary before and after the epidemic in this range. The research of the research group found that, except the graduates whose expected salary before the epidemic was 3,001-5,000 yuan, the expected salary after the epidemic was 3,001-5,000 yuan, and the expected salary before the epidemic was 1,000-3,000 yuan (32.36%), 5,001-8,000 yuan (17.45%) and 10,000 yuan in descending order. Graduates from other groups with expected employment salary of 5,001-8,000 yuan are selected, and the expected employment salary before the epidemic is 8,001-10,000 yuan (28.18%), 3,001-5,000 yuan (13.23%), 1,000-3,000 yuan (3.31%) and 10,001-10 in descending order.
Similarly, graduates from other groups with expected employment salary of 1,000-3,000 yuan after the epidemic were selected, and the expected employment salary before the epidemic was 3,001-5,000 yuan (3.72%), more than 15,000 yuan (1.38%), 5,001-8,000 yuan (0.23%) and 8,001-10,000 yuan in descending order. After the epidemic, the expected salary of other groups of graduates is 8,001-10,000 yuan. From high to low, the expected salary before the epidemic is 10,001-15,000 yuan (24.21%), 5,001-8,000 yuan (5.81%), 15,000 yuan (2.29%) and 1,000-3,000 yuan. After the epidemic, the expected salary for employment was selected as 10,001-15,000 yuan for other graduates. From high to low, the expected salary for employment before the epidemic was 8,001-10,000 yuan (7.23%), more than 15,000 yuan (3.67%), 1,000-3,000 yuan (0.78%) and 5,001-8,000 yuan. After the epidemic, graduates from other groups with expected salary of more than 15,000 were selected. From high to low, the expected salary before the epidemic was 10,001-15,000 yuan (10.32%) and 8,001-10,000 yuan.(1.65%), 1,000-3,000 yuan (1.36%), 5,001-8,000 yuan (0.29%) and 3,001-5,000 yuan (0.15%).
The expected salary of college graduates before and after the epidemic remained relatively stable, but it still showed obvious intermediate agglomeration effect of expected salary after the epidemic. Among the graduates with expected salary changes before and after the epidemic, with 5,000 yuan as the boundary, graduates with employment expectation salary below 5,000 yuan before the epidemic mainly increased to 5,000 yuan after the epidemic, while graduates with employment expectation salary above 5,000 yuan before the epidemic mainly decreased to 5,000 yuan after the epidemic.
The change of unit is "rational", and the change of "kinship" is the main one.
Before the epidemic, the proportion of the nature selection of the employment expectation units of college graduates in China was from high to low: state-owned enterprises (22.24%), junior high school education units (18.44%), medical and health units (13.17%), party and government organs (9.35%), private enterprises (9.21%), other institutions (8.50%) and higher education units (8.50%). Wholly foreign-owned enterprises, 4.90%), scientific research and design units (4.18%), urban communities (0.72%), troops (0.59%) and rural villages (0.33%). After the epidemic, the selection ratio from high to low is state-owned enterprises (21.61%), junior high school education units (18.90%), medical and health units (13.21%), party and government organs (9.84%), private enterprises (9.34%), other institutions (8.92%) and higher education units (7.87%).
On the whole, before and after the epidemic, the expected employment units of college graduates were stable and consistent. The proportion of graduates who expected employment units were state-owned enterprises, higher education units, foreign-funded enterprises and scientific research and design units decreased slightly, while the proportion of graduates who expected employment units were junior education units, medical and health units, party and government organs, private enterprises, other institutions, urban communities, troops and rural villages increased slightly, but the change was not significant.
Looking through the internal structure of the nature selection of employment expectation units for fresh graduates before and after the epidemic, the research group found that the stability of the nature of employment expectation units is medical and health units, middle and early education units, party and government organs, state-owned enterprises, higher education units, other institutions, private enterprises, scientific research and design units, foreign-funded enterprises, urban communities, troops and rural villages in turn. Among them, before and after the epidemic, the stability of the employment expectation unit of fresh graduates was the worst in rural villages. After the epidemic, 65.79% of the graduates chose another employment expectation unit, and the main flows were urban communities, state-owned enterprises, party and government organs, and junior high school education units. 42.65% of the graduates who expected to choose the army before the epidemic mainly flowed to the party and government organs, middle and early education units, state-owned enterprises and higher education units from high to low after the epidemic.
Generally speaking, the changes in the nature of employment expectation units of college graduates before and after the epidemic show the characteristics of "rationalization", and the changes are mainly based on the changes in the nature of "kinship". For example, 25.63% graduates chose state-owned enterprises as the expected employment units before the epidemic, and the changes in the nature of expected units mainly flowed to private enterprises; Before the epidemic, 33.27% chose private enterprises as graduates of expected employment units, and the nature of the expected units changed mainly to state-owned enterprises; Before the epidemic, 12.40% of the graduates were selected from junior high school education units as expected employment units, and the nature of the expected units changed mainly to other institutions and higher education units; Before the epidemic, 28.75% of the graduates chose higher education units as expected employment units, and the nature of the expected units changed mainly to middle and junior education units.
Education, health and social work have the smallest fluctuations, and the stability of real estate, accommodation and catering industry is at the bottom.
Before the epidemic, the proportion of employment expectations of college graduates in China was education (32.48%). Health and social work (13.14%); Financial industry (8.88%), information transmission, software and information technology services (8.15%); Culture, sports and entertainment (7.04%); Manufacturing (5.67%); Public management, social security and social organizations (4.87%); Scientific research and technical services (2.97%); Electricity, heat, gas and water production and supply industries (2.84%); Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery (2.39%); Construction industry (2.17%); Wholesale and retail (1.90%); Transportation, warehousing and postal services (1.61%); Accommodation and catering industry (1.47%); Water conservancy, environment and public facilities management (1.13%); Real estate (0.79%); Leasing and business services (0.71%); Army (0.69%); Residential services, construction and other services (0.48%); Mining industry (0.35%); International organizations (0.27%).
Education (33.23%) ranked from high to low after the epidemic. Health and social work (13.42%); Information transmission, software and information technology services (8.11%); Financial industry (7.85%); Culture, sports and entertainment (6.36%); Public management, social security and social organizations (5.72%); Manufacturing (5.59%); Electricity, heat, gas and water production and supply industries (3.02%); Scientific research and technical services (2.81%); Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery (2.37%); Construction industry (2.02%); Wholesale and retail (1.87%); Transportation, warehousing and postal services (1.56%); Accommodation and catering industry (1.23%); Water conservancy, environment and public facilities management (1.13%); Army (0.91%); Real estate (0.74%); Leasing and business services (0.67%); Mining industry (0.55%); Residential services, construction and other services (0.54%); International organizations (0.31%).
Generally speaking, there is little change before and after the epidemic. Education, health and social work, information transmission, software and information technology services, financial industry, culture, sports and entertainment are the top five most popular employment expectations for college graduates. Leasing and business services, mining, residents’ services, construction and other services, and international organizations are the last four career choices for college graduates.
The research group analyzed the internal structure of the choice of employment expectation industries for college graduates in China before and after the epidemic, and found that the stability of employment expectation industries from high to low is: health and social work, education, information transmission, software and information technology services, manufacturing, finance, electricity, heat, gas and water production and supply, public management, social security and social organizations, water conservancy, environment and public facilities management, culture, sports and entertainment, and construction. Scientific research and technical services, transportation, warehousing and postal services, agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, fishery, military, international organizations, residential services, repairs and other services, wholesale and retail, mining, leasing and business services, accommodation and catering, real estate.
Before and after the epidemic, employment expectations were relatively poor in real estate, accommodation and catering, and leasing and business services. After the epidemic, graduates chose education, finance, information transmission, software and information technology services, and the proportion was relatively higher. The education, health and social work industries have become the industries with the least fluctuation, the strongest stability and the least outflow before and after the epidemic, but with the highest inflow willingness.
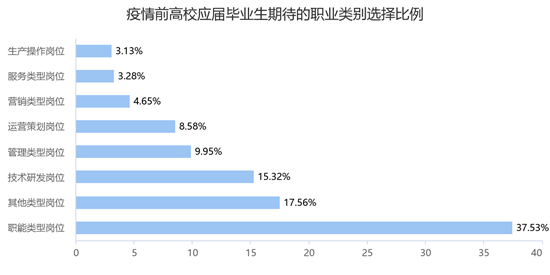
Marketing type jobs have the worst stability, and functional type jobs are the most popular.
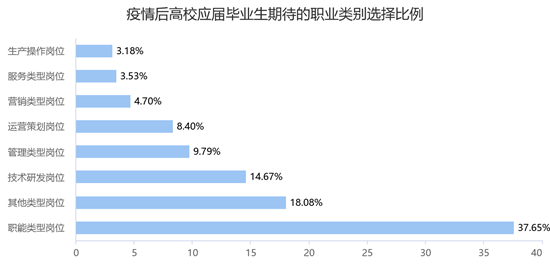
Before the epidemic, the proportion of career categories that fresh graduates expected from high to low was functional positions (such as administration, personnel and finance, 37.53%), other positions (17.56%), technical research and development positions (such as R&D engineers and testing, 15.32%), management positions (9.95%) and operation planning positions (such as operations, products and operations) The post-epidemic situation is completely consistent with that before the epidemic situation, and the selection ratio from high to low is functional posts (37.65%), other posts (18.08%), technology research and development posts (14.67%), management posts (9.79%), operation planning posts (8.40%), service posts (3.53%) and production operation posts.
Among the job categories expected by graduates after the epidemic, the selection proportion of functional posts, other types of posts, marketing posts, service posts and production operation posts increased slightly, while the selection proportion of technology research and development posts, management posts and operation planning posts decreased slightly, but the change was still not significant.
Before and after the epidemic, the stability of employment expectations of college graduates from high to low is: other types of jobs, functional types of jobs, technology research and development jobs, operation planning jobs, management types of jobs, service types of jobs, production operation jobs, marketing types of jobs. Among them, the stability of marketing jobs is the worst, with 42.96% of graduates who chose this job before the epidemic, and the expected jobs selected after the epidemic are mainly functional jobs, technology research and development jobs, operation planning jobs and management jobs from high to low. Functional jobs are the most popular occupational category for fresh graduates before and after the epidemic, and the absolute number of job category choices, stability and inflow attraction rate for graduates after the epidemic are the highest.
(The author is a professor at Northeast Normal University and a top-notch young talent in the National Ten Thousand Talents Program.)