Radio Documentary Literature "Liangjiahe" Episode 10: Be a Giant in Action
36.8 north latitude,
On the Loess Plateau in northern Shaanxi,
There is a small village,
Name is Liangjiahe,
"This is a place of great learning." ……
Tell the story of the educated youth life of the Supreme Leader General Secretary in Liangjiahe,
Pursuing the initial heart of the people’s leaders;
Record the earth-shaking changes of Liangjiahe for decades,
Inspire the confidence to move forward.
The Central Radio and Television General Station was grandly launched.
12 episodes of radio documentary literature "Liangjiahe"
Episode 10: Be a giant in action
Click on the audio to listen immediately.
"Iron Lock" Wu Hui
"Tiesuo" is Wu Hui’s nickname.
"Come on, little friend, come in!" Inside the cave, the educated youth whispered to Wu Hui outside the cave.
Wu Hui didn’t move, and he didn’t know what to say in rags. In fact, he is not a child, but he is thin and looks small.

Wu hui
That year, Wu Hui was 14 years old, only one year younger than the supreme leader. Before the arrival of educated youth, he had just returned to Liangjiahe from school. He is a junior high school student.
Wu Hui didn’t go in and stood at the door listening to them. He looked at the educated youth as if he were looking at a new world.
At that time, it was the cold winter and the weather was very cold, but the educated youth couldn’t burn the kang. The cave was as cold as icehouse. The educated youth asked Wu Hui outside the door if he would burn the kang. Wu Hui said, "Of course." In the countryside, which doll can’t burn kang? Wu Hui timidly walked into the cave.
In this way, Wu Hui became a frequent visitor in the cave of educated youth. The educated youth knew his nickname "Tiesuo", and he also remembered the names of six educated youth.
Wu Hui has seven brothers and sisters. The family has a large population and little labor. At that time, such families were the poorest in the countryside.
Wu Hui’s nickname "Iron Lock" hides a bitter story. Wu Hui once had a brother who died soon after his birth. Wu Hui was also sickly after his birth, so his parents asked the fortune teller to "keep the lock" for him, so he was nicknamed "Iron Lock".
"Keeping locks" is a custom in northern Shaanxi. When a child is weak and sick after birth, it is necessary to "protect the lock" to eliminate disasters and take refuge. Children who are "locked" and have a good family usually wear a silver lock; Ordinary people usually use 12 thimbles to string together as locks. This lock will be worn until the 12th birthday, and then an "unlocking" ceremony will be held.
Wu Hui is still very thin after the "unlocking". Although he was born in the countryside, it is difficult for him to adapt to the heavy labor in the countryside. Even if weeding is the lightest job for others, Wu Hui can’t stand it. He often ran to the ditch to sit on the pretext of relieving himself, and didn’t go back to work until the captain called him. At first, he earned 6 points like educated youth, and later improved, but never reached 10 points.
"Translator" Wu Hui
Wu Hui is small, but he is smart. He is happy to help educated youth and villagers eliminate language barriers. Wu Hui studied Mandarin at school, and the educated youth asked him if he didn’t understand Yanchuan dialect, so he became the "translator" of the educated youth.
The role of "translator" has added a lot of confidence to Wu Hui. Because they don’t live far from each other, Wu Hui comes to the educated youth whenever he has the chance. In addition to listening to the educated youth chatting, what attracts him more is the books placed on the kang platform, windowsill and pillow.

In 1973, the supreme leader and Beijing educated youth Lei Pingsheng (first from left), Tao Haisu (second from right) and Lei Rongsheng (first from right) were in Yanchuan County.
In the past few years at school, he has hardly read any extracurricular books except textbooks, and he has never seen so many books as thick as bricks. At first, he carefully picked up a book on the kang and looked through it page by page. When the educated youth saw that he liked reading, they said to him, "Take it if you like."
The first book he borrowed was 100,000 Why brought by the Supreme Leader. "How amazing it is to know a hundred thousand reasons!" Wu Hui My Sweetie in my heart, walking also look up.
This book opened a window for him to know the wide world. He was so hungry and excited that he couldn’t bear to let go. When he was hungry, he chewed bran dumplings and held a book, feeling that bran dumplings that were usually difficult to swallow were much better.
After reading 100,000 Why, he borrowed Romance of the Three Kingdoms, Mother, Quiet Don River and so on from the Supreme Leader. He began to have spiritual communication with the educated youth.
He felt frankness and frankness from Wang Yansheng and Lei Pingsheng, and low-key and pragmatic from the supreme leader. Wu Hui said: "I admire them. They are actually the coordinates of my life."
Wu Hui feels that it is reading that gives the supreme leader unlimited power. The supreme leader said: "There is a wider world and more knowledge in the book. Through learning, people will increase their knowledge and gain knowledge, and they will become stronger and stronger."
Under the influence of the supreme leader, Wu Hui swam in the ocean of knowledge and gradually strengthened his determination to go to college.
In 1973, he and the supreme leader entered the university together. The results came out, and he was admitted to Yan ‘an Normal School.
When Wu Hui went to school, the Supreme Leader gave him a 30-Jin food stamp, and took out a blue fur collar coat left by Wang Yansheng when he left Liangjiahe. He said to him, "Take this coat, and you can wear it at school and use it as a quilt cover."
Be a giant in action: President Wu Hui.
When Wu Hui graduated, the supreme leader had left Liangjiahe. Wu Hui was first assigned to the May 7th Middle School of Wen ‘anyi Commune as the teaching director, then transferred to the teaching and research section of Yanchuan County, and then went down to the grassroots level, successively serving as the education specialist in Chengguan Town, Wen ‘anyi Town and Yuju Township. But no matter where he goes, he asks himself to talk less and do more, and be a giant in action.
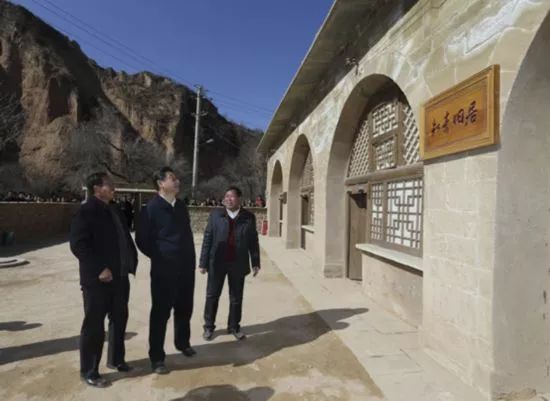

In 1970, the production team specially built 6-hole educated youth caves. The supreme leader moved there until he left in 1975. The picture shows the top leaders visiting Shaanxi in 2015.
In 1987, Wu Hui was transferred to the head of Yuzhong School. He didn’t expect Yuju Middle School to be completely different from what he imagined: the doors and windows of the classroom were tattered, creaking in the wind, garbage was piled up on the campus, weeds were growing, and bricks and gravel were scattered all over the floor … …
Wu Hui understands that this is the teacher’s heart is scattered and confidence is gone! This is parents’ disappointment with the school!
The new official took office with three fires, and Wu Hui’s first fire was to rectify the school order. He formulated strict discipline and took the lead in implementing it himself. The school gate, playground and classroom are all his supervision posts.
He stood at the school gate to see which teacher was late and which student left early!
He stood on the playground to see which class shouted loudly and which queue kept pace!
He stood in the classroom to see which teacher gave a wonderful lecture and which student raised his hand actively!
He stood on the rostrum of the teacher-student conference of the whole school, commending the advanced, rewarding the excellent, criticizing the backward and punishing the violation of discipline.
In less than a month, teachers and students can do morning exercises on time, reading in the morning sounds loud, the classroom is active, self-study is quiet, students are in formation after school, and teachers are energetic in class … … Yuju Middle School has finally taken on the appearance of a school.
Wu Hui knows that the key to measure the quality of a school lies in the quality of teaching. He set an example, set a benchmark, organized teaching observation, rewarded diligence and punished laziness, and the enthusiasm of teachers was mobilized, and the teaching work in Yuju Middle School quickly stepped on the right track.
In the second year, Wu Hui took a teacher to Yan ‘an Education Bureau to apply for a teaching building construction project, which was quickly implemented. Soon, a brand-new teaching building stood on the campus of Yuju Middle School. He ran to the township and county for support, equipped with teaching equipment, and the teachers and students moved into the new teaching building with joy.
Yuju Middle School has changed, both inside and outside. People say: "It is not easy for Yuju Middle School to be in the forefront of township middle schools in the county."
There are still many difficult things. In 1993, Wu Hui was transferred to the position of director of the Education Committee of Yongping Town, just as the county was paying close attention to the "sixth grade", requiring rural schools in towns and villages to have classrooms and desks and stools for everyone, and the enrollment rate must reach 99%.
Wu Hui told Yongping village branch secretary and village director: "It can attract social forces to join and improve the school’s running conditions."
On hearing this, Wu Hui, secretary of the village branch and director of the village, was right, so he and Yanchang Oil Company formed a co-construction unit and soon built a five-story teaching building, and Yongping Village passed the "sixth grade" pass.
According to the same idea, Yongping Town raised funds from various sources, and all schools achieved the "sixth grade" standard.
In 2000, Wu Hui was transferred to Yongping Middle School as the general manager. In the past four years, he worked with the school leaders to plan, run projects, find funds, coordinate and supervise, without stopping. An apartment building, a teaching building and a dining building have sprung up one after another … … Finally, Yongping Middle School was completely changed.
In 2014, Wu Hui retired. Before he left, he came to the campus alone, walking east and looking west, reluctant to leave.
"A man’s life should be spent like this: looking back, he will not regret for wasting his time, nor will he be ashamed for doing nothing … …” Wu Hui thought that he didn’t live up to the meaning of life!
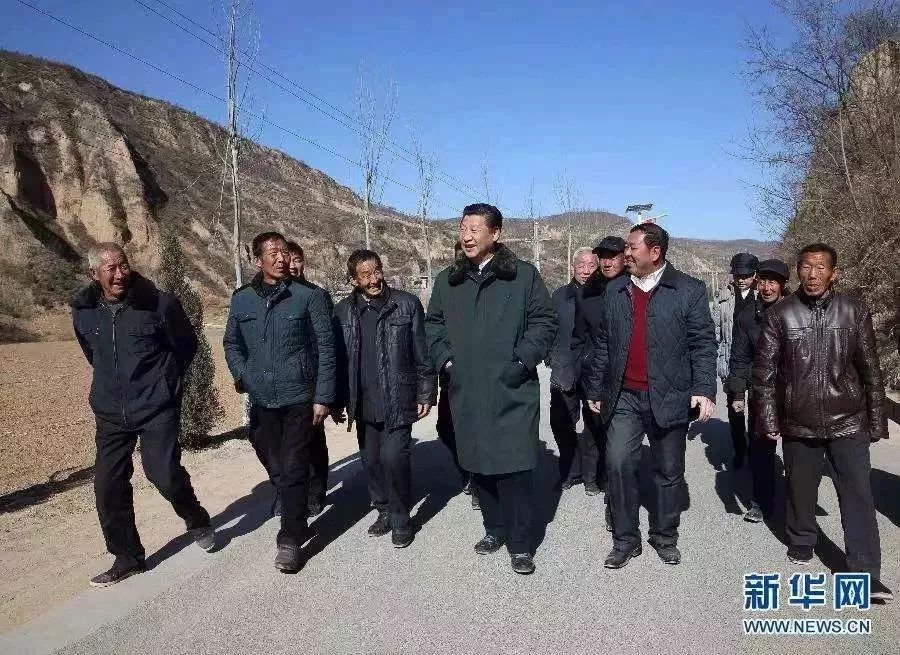


On the morning of February 13th, 2015, the Supreme Leader visited the villagers in Liangjiahe Village, Wen ‘anyi Town, Yanchuan County, Yan ‘an City, and conducted field research on poverty alleviation in the old district. Xinhua News Agency reporter Lan Hongguang photo