Gao Shengqing, Liu Hua, et al.: Method and application of collaborative evaluation of transportation and land space —— Taking Guangzhou as an example
The following article comes from urban planning, and the author clicks on attention >

Urban planning.
Urban Planning, founded in 1977, is a sci-tech periodical sponsored by urban planning society of china. It is a national Chinese core periodical, a China science and technology core periodical, a China humanities and social sciences core periodical, a top 100 science and technology periodical, and a top-quality science and technology periodical.
This article is reproduced from urban planning (ID: chengshiguihuazazhi).
Text | Gao Shengqing Liu Hua Gu Yuxi Liu Mingmin Wang Xinning
Traffic evaluation is an important basic work to support the formulation of traffic plan. Under the background of the publication of "Guidelines for the Compilation of Municipal Land and Space Master Plan", traffic evaluation is faced with new requirements of "planning zoning" and new challenges of how to reflect the role of "feedback leading" in traffic. Studying the interactive relationship between traffic and land spatial zoning, determining the dominant traffic demand mode of different land spatial zoning, and establishing technical methods including qualitative collaboration, quantitative collaboration, weight determination and collaborative evaluation are helpful to implement the planning zoning idea and give play to the leading role of traffic support.
1 research origin
Planning zoning has become one of the ideas that traffic planning needs to follow. The Guide to the Compilation of Municipal Land and Space Master Plan puts forward the concept of planning zoning and requires "defining the development goal and zoning strategy of comprehensive transportation system". This requires, in the traffic evaluation, on the one hand, to continue the past "evaluation" including public transport, roads, tracks, slow travel, etc., to support the traffic development goals and scheme formulation; On the other hand, we should also follow the idea of planning zoning, carry out "area evaluation" between transportation and different land spatial zoning, study the interactive relationship between transportation and space, industry, land use, etc., make clear the dominant transportation demand modes of different spatial zoning, and give priority to meeting them, so as to implement the requirements of "comprehensive carrying capacity" and support the formulation of zoning strategies and schemes.
The feedback and leading role of traffic in cities should be further improved. The formulation and evaluation of traffic schemes are mostly based on the overall urban planning and regulatory detailed planning, which reflects the supporting role of traffic to the city, but also reflects that traffic is in a passive state from the side, and it is difficult to effectively guide and feedback the land use classification and industrial functions of the city. The Guide also proposes to carry out research on the impact of transportation system and information technology on regional spatial development and countermeasures, optimize the structure and layout of construction land, and promote the integrated development of people, cities, production and transportation. This requires the collaborative evaluation of transportation and land space, the establishment of the interactive relationship between transportation and land space, and the formation of a two-way adjustment mechanism. When the existing dominant mode of transportation (speed or capacity) in the national spatial division lags behind the dominant mode of transportation it needs, the transportation facilities should be improved or the function and development intensity of the space industry should be reduced; When the existing dominant mode of transportation in the national land spatial division is ahead of the dominant mode of transportation it needs, the spatial function should be improved and the industrial upgrading should be promoted.
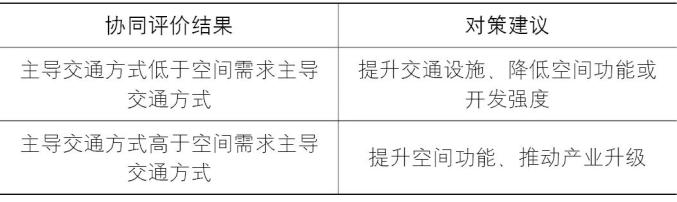
▲ Table | Collaborative Evaluation of Transportation and Land Space
2 technical requirements for collaborative evaluation
Continuity: Collaborative evaluation is a supplement to the existing traffic evaluation methods, and the existing mature urban traffic models should be fully utilized in the evaluation process.
Relevance: Collaborative evaluation is based on the corresponding relationship between traffic, zoning space and industrial function, which fully reflects the requirements of different zoning spaces for leading traffic modes and the priority of traffic response.
Comprehensive: Collaborative evaluation is not an evaluation that reflects a single traffic index, but a comprehensive evaluation that includes multiple leading traffic mode indicators. In the evaluation process, the corresponding weights are different according to the different importance of leading modes of transportation.
Feedback: Collaborative evaluation not only effectively reflects whether the scheme meets the needs of national land, space and industrial functions, but also can effectively identify the spillover effect of traffic on the city, reflecting the feedback leading role of traffic on industrial functions and spatial development.
3 technical methods of collaborative evaluation
The technical methods of collaborative evaluation include qualitative collaboration, quantitative collaboration, weight determination and collaborative evaluation.
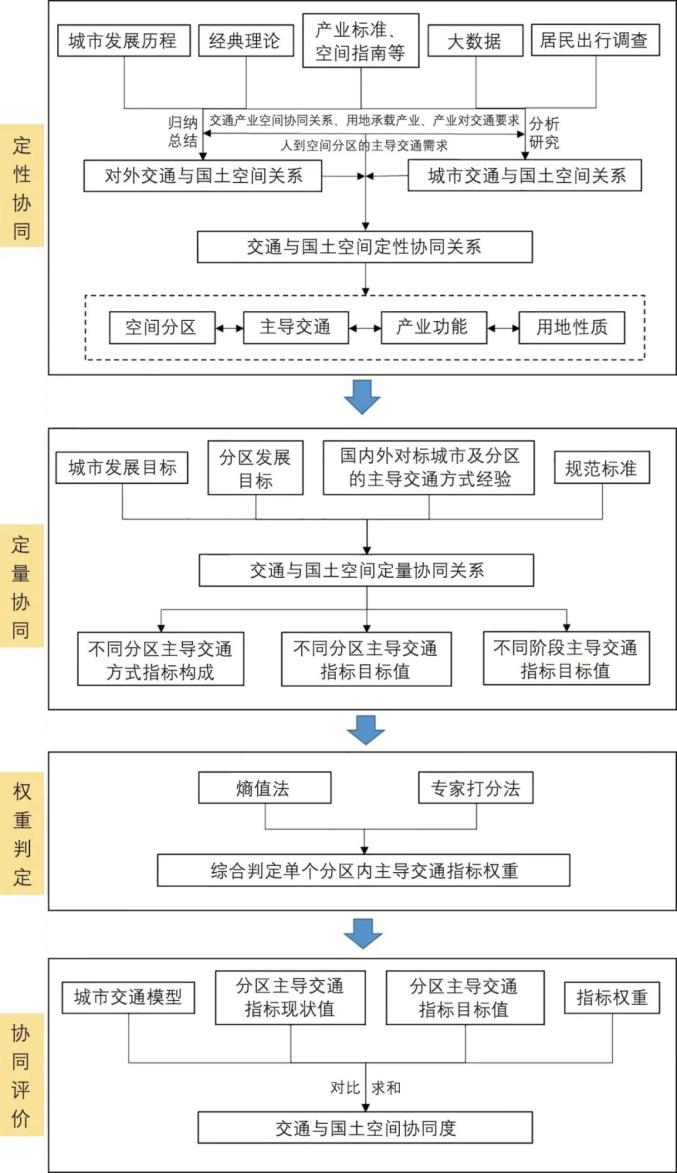
▲ Figure | Traffic and Land Spatial Collaborative Evaluation Method Process
3.1 Qualitative synergy
By combing the urban development process, analyzing big data and studying the data of residents’ trip survey, we fully consider the requirements of industry for land use, industry for transportation and people for transportation, and summarize the corresponding relationships between different industrial spaces and external transportation (ports, railways, highways, airports, etc.) and urban transportation (tracks, conventional public transportation, cars, walking and bicycles, etc.), and establish the land spatial division, dominant transportation mode and land use nature.
3.2 Quantitative synergy
Combined with the national economic and social development planning, municipal land space planning, etc., this paper studies the target cities and related norms and standards at home and abroad, puts forward the composition and target value of leading transportation mode indicators, and establishes the cooperative relationship between land space division and transportation quantity. In the process of research, we should fully consider the differences in location and development stages of the same type of zoning and reasonably determine the target value.
3.3 Weight Determination
Through entropy method, expert scoring method, etc., the weight values of several leading traffic indicators in different land spatial divisions are comprehensively judged.
3.4 Collaborative evaluation
With the help of urban traffic model, the status quo value of leading traffic indicators in different land spatial divisions is calculated by taking traffic districts as a unit, and compared with the target value of leading traffic indicators determined by quantitative collaboration, combined with the weight ratio, the degree of collaboration between traffic and different land spatial divisions is summarized to complete the collaborative evaluation.
4 the practical application of collaborative evaluation
4.1 Guangzhou traffic and land space qualitative synergy
Based on Guangzhou’s urban development history, traffic survey data and big data, from the perspective of traffic support leading industrial development and fully serving people’s travel, combined with the Classification of National Economy Industries, Guidelines for the Compilation of Municipal Land Space Master Plan and Guidelines for the Classification of Land Use for Land Space Survey, Planning and Use Control, the qualitative correspondence between Guangzhou’s traffic and land space is established, and agricultural production, industrial production, logistics and warehousing, productive services and non-public services are formed. Under the scale of traffic community, using ArcGIS and traffic model software, Guangzhou is divided into nine types of land space.

▲ Table |
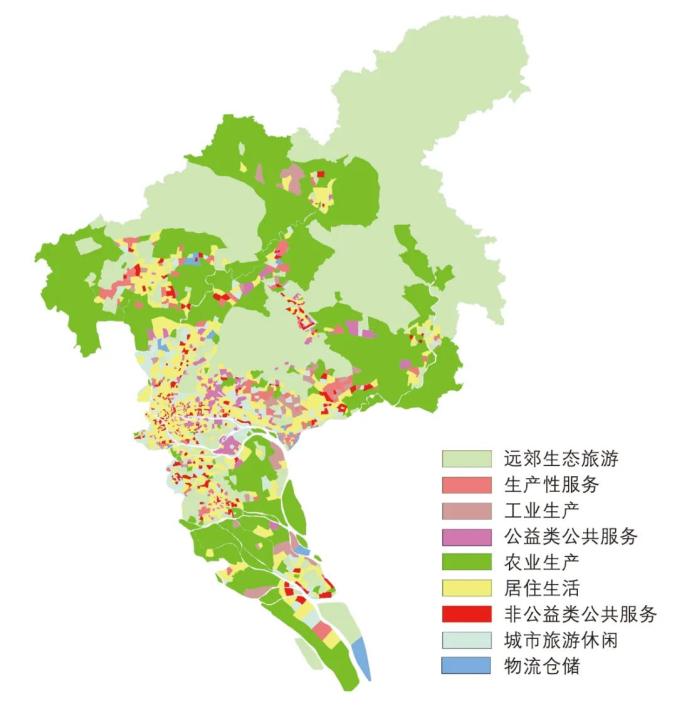
▲ Figure | Spatial distribution of Guangzhou’s current national territory
4.2 Guangzhou traffic and land space quantitative collaboration
When making strategic plans for urban development, land space planning and transportation development, Guangzhou mostly targets Beijing, Shanghai, Hongkong, new york, London, Tokyo, Singapore and other global central cities. By studying the leading traffic indicators of these cities’ land space, combined with Guangzhou’s own urban characteristics and relevant domestic and foreign norms, the target values of leading traffic indicators of different land space divisions are determined.

▲ Table | Leading traffic indicators of Guangzhou’s land space
4.3 Guangzhou traffic and land space collaborative evaluation
With the help of Guangzhou urban traffic model, this paper calculates the status quo value of leading traffic mode indicators in different land and space divisions, and compares it with the target value of leading traffic indicators determined above (the differences of target values in different regions and different development stages should be fully considered), and carries out collaborative evaluation with weights, so as to obtain the results of collaborative evaluation of traffic and space in Guangzhou and the results of collaborative evaluation of different types of spaces.
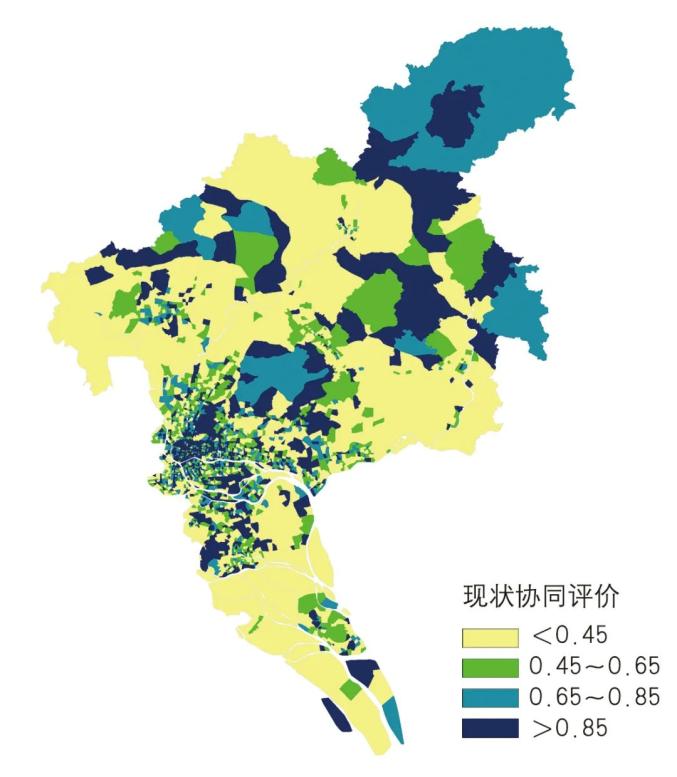
▲ Figure | Guangzhou Traffic and Space Collaborative Evaluation Results
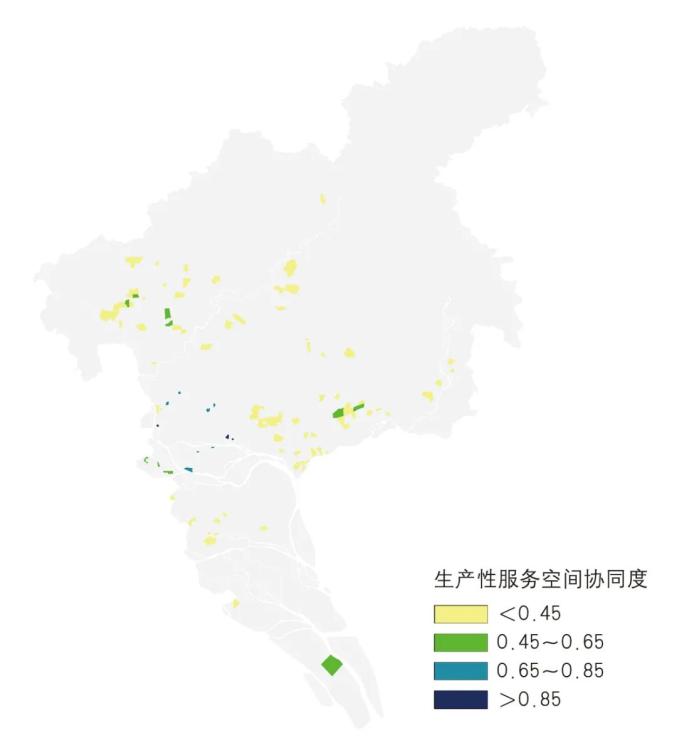
▲ Figure | Results of collaborative evaluation of productive service space
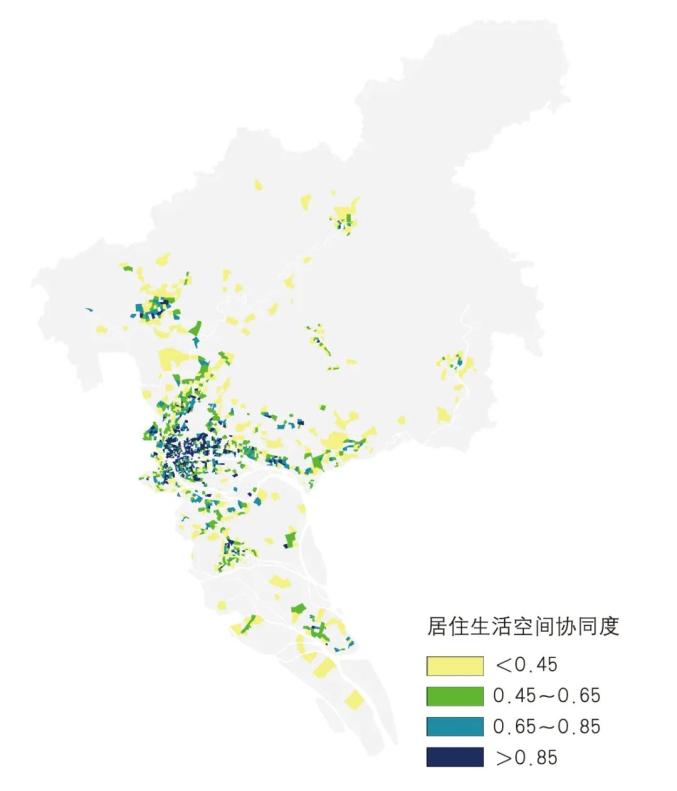
▲ Figure | Results of collaborative evaluation of residential and living space
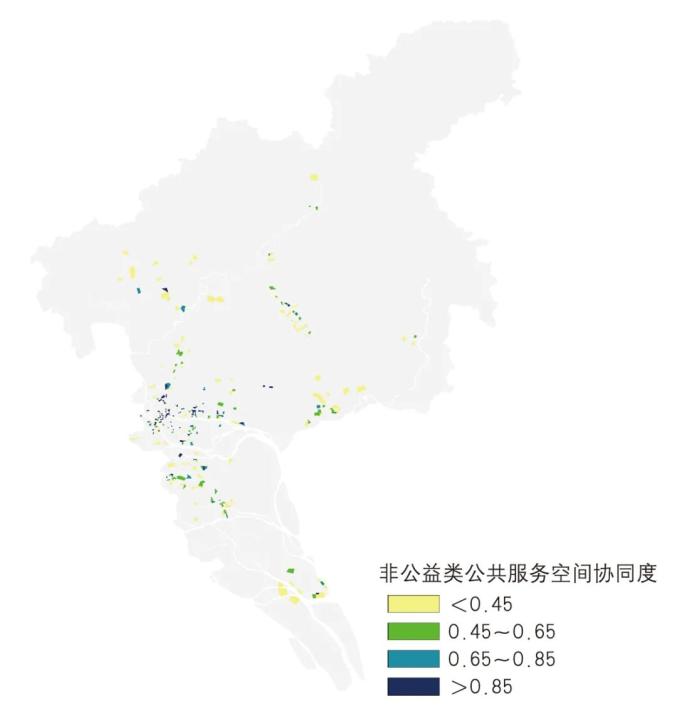
▲ Figure | Non-public space collaborative evaluation results
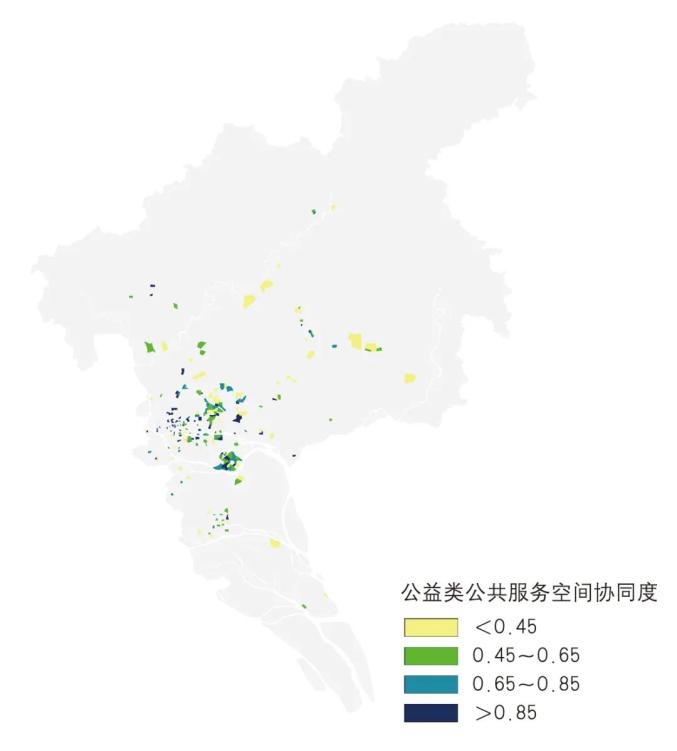
▲ Figure | The results of public welfare spatial collaborative evaluation
5 Conclusion
The technical method of collaborative evaluation of transportation and land space under the idea of zoning is the continuation of "double evaluation" put forward in "Several Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Establishing Land Space Planning System and Supervising its Implementation", the implementation of the idea of "planning zoning" put forward in "Guidelines for the Compilation of Municipal Land Space Master Plan", and an innovative exploration on how to construct a transportation planning method suitable for land zoning space.
The original intention of this paper is not to ask cities to carry out standardized and unified traffic planning and design, but to try to embody the role of "supporting, feedback and leading traffic" at the operational level. Based on the collaborative evaluation of the correspondence between traffic and national space, on the one hand, from the perspective of national space, it identifies the problems existing in the leading mode, layout scheme, scale and capacity of traffic, emphasizes the priority response to the leading traffic demand, and gives full play to the supporting role of traffic; On the other hand, from the perspective of transportation, it also identifies the problems existing in the functional orientation, land use classification, industrial direction, etc., promotes its optimization and adjustment, and gives play to the leading role of transportation feedback. The collaborative evaluation of several leading traffic indicators is a complement to the current evaluation methods of roads, buses and tracks, and also fully reflects the requirements of "comprehensive carrying capacity".
Written by Gao Shengqing and Wang Xinning
Original introduction:
The method and application of collaborative evaluation of transportation and land space —— Taking Guangzhou as an example was published in Urban Planning, No.9, 2021, pp. 35-45.
Gao Shengqing, master, chief engineer, senior engineer, and author of this article, is the traffic office of China City and Small Town Reform and Development Center.
Liu Hua, master, engineer of China City and Small Town Reform and Development Center.
Gu Yuxin, master, senior engineer of Guangzhou Transportation Planning and Research Institute.
Liu Mingmin, bachelor, senior engineer of Guangzhou Transportation Planning and Research Institute.
Wang Xinning, master, engineer of China City and Small Town Reform and Development Center.
[Full-text Download] The article has been published on HowNet. Copy and search the following URL, or click "Read the original" below to download and read the full text.
https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx? dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDAUTO&filename=CSGH202109006&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=e0VWQrSXHmR4C4xbJ3syKVYJLm8Zo5swY6l%25mmd2F0X46YIeS1gjBtq7MPvrtCD9f1GZy
Source: urban planning
Note: This article reproduced in WeChat official account is only for sharing, not for any commercial use. If copyright issues are involved, please contact backstage to authorize or negotiate cooperation, and we will handle them properly for you as soon as possible in accordance with the copyright law.
————————————
Original title: Gao Shengqing, Liu Hua, et al.: Method and application of collaborative evaluation of transportation and land space —— Taking Guangzhou as an example.
Read the original text