China’s national defense in the new era.
Xinhua News Agency, Beijing, July 24th, the State Council Press Office published a white paper entitled "China’s National Defense in the New Era" on July 24th. The full text is as follows:
China’s national defense in the new era.
People’s Republic of China (PRC)
the State Council Information Office
(July 2019)
catalogue
foreword
I. International security situation
Second, China’s defensive national defense policy in the new era
Third, fulfill the mission of the army in the new era
Fourth, China’s national defense and army in reform.
V. Reasonable and moderate defense expenditure
Sixth, actively serve and build a community of human destiny
Concluding remarks
foreword
In today’s world, mankind has increasingly become a community of destiny with mixed interests, safety and common prosperity. Today, China is in the critical stage of building a well-off society in an all-round way and starting a new journey of building a socialist modern country in an all-round way, and Socialism with Chinese characteristics has entered a new era.
In order to declare China’s defensive national defense policy in the new era, introduce China’s practice, purpose and significance of building a consolidated national defense and a strong army, and enhance the international community’s understanding of China’s national defense, the China government published a white paper entitled "China’s National Defense in the New Era".
I. International security situation
Today, the world is experiencing a great change that has never happened in a century. World multipolarization, economic globalization, social informationization and cultural diversity are developing in depth. The trend of the times of peace, development, cooperation and win-win is irreversible, but the instability and uncertainty facing international security are more prominent, and the world is not peaceful.
The international strategic pattern has undergone profound evolution.
The international forces have accelerated the division and combination, the strength of emerging market countries and developing countries has continued to rise, and the strategic forces have become more balanced. Promoting peace, stability and development have become the universal demands of the international community, and the rise of peace forces far exceeds the growth of war factors. However, hegemonism, power politics and unilateralism have risen from time to time, regional conflicts and local wars have continued, and the international security system and order have been impacted.
International strategic competition is on the rise. The United States has adjusted its national security strategy and national defense strategy, pursued a unilateralist policy, provoked and intensified competition among major powers, substantially increased military spending, accelerated the upgrading of its capabilities in the fields of nuclear, space, network and missile defense, and undermined global strategic stability. NATO continued to expand its membership, strengthened its military deployment in Central and Eastern Europe and held frequent military exercises. Russia strengthens its nuclear and non-nuclear strategic containment capabilities and strives to safeguard its strategic security space and its own interests. The tendency of the EU to independently safeguard its own security has increased, and the integration of security and defense has been accelerated.
Global and regional security issues continue to increase. International arms control and disarmament have suffered setbacks, and the trend of arms race has emerged. The situation of preventing the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction is complicated, and the international non-proliferation mechanism is endangered by pragmatism and double standards and faces new challenges. Extremism and terrorism continue to spread, and non-traditional security threats such as cyber security, bio-security and piracy are increasingly prominent. There have been twists and turns in the settlement of the Iranian nuclear issue, and the political settlement of the Syrian issue still faces difficulties. The integration, relevance and interactivity of national security are constantly increasing, and no country can deal with it independently or be immune to it.
The security situation in the Asia-Pacific region is generally stable.
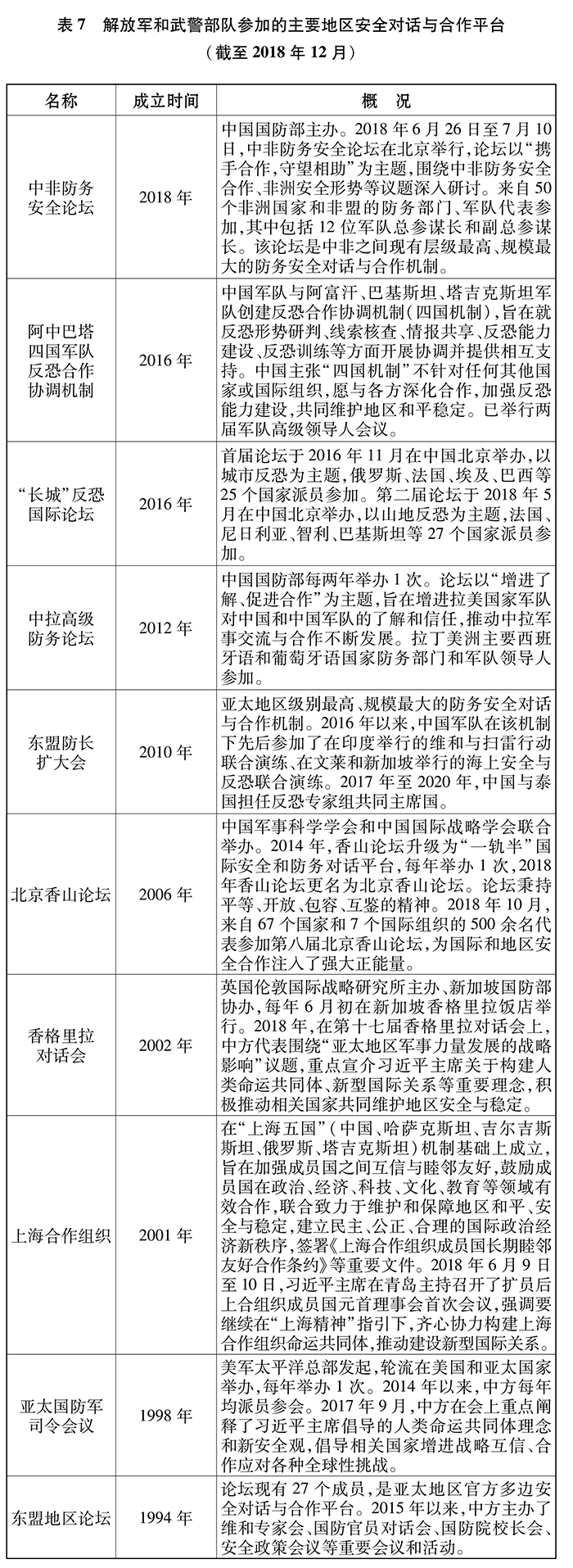
The awareness of the community of destiny of Asia-Pacific countries has increased, and handling differences and disputes through dialogue and consultation has become the main policy orientation, promoting the region to become a stable plate in the global pattern. The Shanghai Cooperation Organization builds a constructive partnership of non-alignment, non-confrontation and non-targeting at third parties, expands cooperation in the field of defense and security, and creates a new model of regional security cooperation. The China-ASEAN Defense Ministers’ Informal Meeting and the ASEAN Defense Ministers’ Expansion Meeting have played an active role in promoting mutual trust by strengthening military exchanges and cooperation. The situation in the South China Sea has stabilized and improved, and countries in the region have properly managed risk differences. Cooperation in regional and national anti-terrorism coordination mechanisms has been deepened. A balanced, stable, open and inclusive security architecture with Asian characteristics is constantly developing.
The focus of the world economy and strategy continues to shift to the Asia-Pacific region, which has become the focus of the big country game, bringing uncertainty to regional security. The United States has strengthened its military alliance in the Asia-Pacific region, increased its military deployment and intervention, and added complicated factors to Asia-Pacific security. The deployment of the "Sade" anti-missile system by the United States in South Korea has seriously undermined the regional strategic balance and seriously damaged the strategic security interests of regional countries. Japan adjusted its military security policy, increased investment, sought to break through the "post-war system", and its military extroversion was enhanced. Australia continues to consolidate its military alliance with the United States and strengthen its military participation in the Asia-Pacific region in an attempt to play a greater role in security affairs.
Regional hot spots and controversial issues still exist. The situation on the Korean peninsula has eased, but there are still uncertainties. The situation in South Asia is generally stable, but conflicts between India and Pakistan occur from time to time, and political reconciliation and reconstruction in Afghanistan are difficult to advance. Disputes over territorial and maritime rights and interests among some countries, ethnic and religious contradictions and other issues still exist, and hot issues of regional security arise from time to time.
The risks and challenges facing national security cannot be ignored.
China continues to maintain a good situation of political stability, national unity and social stability, and its comprehensive national strength, international influence and ability to resist risks have been significantly enhanced. It is still in an important period of strategic opportunities for development, and at the same time, it faces multiple and complex security threats and challenges.
The situation of the anti-secession struggle is even more severe. The Democratic Progressive Party authorities stubbornly adhere to the "Taiwan independence" separatist stance, refuse to recognize the "1992 Consensus" which embodies the one-China principle, step up the implementation of "de-China" and "gradual Taiwan independence", and attempt to promote "legal Taiwan independence", strengthen hostile confrontation, and rely on foreign self-respect to go further and further on the road of secession. The "Taiwan independence" separatist forces and their activities have always been the biggest real threat to peace and stability in the Taiwan Strait and the biggest obstacle to the peaceful reunification of the motherland. Foreign separatist forces such as "Tibet independence" and "East Turkistan" have frequent activities, which pose a threat to national security and social stability.
Homeland security is still threatened, land boundary disputes have not been completely resolved, island territorial issues and maritime delimitation disputes still exist, and ships and aircraft from some foreign countries frequently carry out close reconnaissance on China, and illegally invade China’s territorial waters and the sea and airspace adjacent to relevant islands and reefs for many times, endangering China’s national security.
China’s overseas interests are threatened by international and regional turmoil, terrorism, piracy and other real threats, and its overseas institutions, overseas enterprises and personnel have been attacked many times. The threat of space and network security is increasingly apparent, and the harm of non-traditional security issues such as natural disasters and major epidemics is rising.
International military competition is becoming increasingly fierce.
Major countries in the world have adjusted their security and military strategies, adjusted their military organizational forms, developed new combat forces, and seized the commanding heights of military competition strategy. The United States carries out military technology and system innovation to seek absolute military superiority. Russia has further promoted the "new look" military reform, and Britain, France, Germany, Japan, India and other countries are adjusting and optimizing their military power systems.
Driven by the new round of scientific and technological revolution and industrial transformation, cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum information, big data, cloud computing and Internet of Things have been applied to the military field at an accelerated pace, and the international military competition pattern is undergoing historic changes. With the rapid development of military high-tech with information technology as the core, the trend of remote precision, intelligence, stealth and unmanned weapons and equipment is more obvious, and the war form is accelerating to evolve into information war, and intelligent war is beginning to emerge.
Significant progress has been made in the military reform with China characteristics, but the task of mechanization construction has not been completed yet, and the level of informatization needs to be improved urgently. Military security is at risk of technical surprise and the gap between military modernization and national security needs is still far behind, and there is still a big gap between the level of military modernization and the advanced military level in the world.
Second, China’s defensive national defense policy in the new era
China’s nature as a socialist country, its strategic choice of taking the road of peaceful development, its independent foreign policy of peace and the Chinese cultural tradition of "harmony is the most important thing" determine that China will always pursue a defensive national defense policy.
Resolutely defend national sovereignty, security and development interests.
This is the fundamental goal of China’s national defense in the new era.
Deter and resist aggression, safeguard national political security, people’s safety and social stability, oppose and contain "Taiwan independence", crack down on separatist forces such as "Tibet independence" and "East Turkistan", and safeguard national sovereignty, unity, territorial integrity and security. Safeguard national maritime rights and interests, safeguard national security interests in space, electromagnetism and cyberspace, safeguard national overseas interests and support national sustainable development.
China firmly upholds national sovereignty and territorial integrity. The South China Sea Islands, Diaoyu Island and its affiliated islands are China’s inherent territory. China’s infrastructure construction in the South Island Reef, deployment of necessary defensive forces and cruising in the Diaoyu Islands waters in the East China Sea are the exercise of national sovereignty according to law. China is committed to resolving relevant disputes through negotiation and consultation with the countries directly concerned on the basis of respecting historical facts and international law. China insists on maintaining peace and stability together with countries in the region, firmly safeguarding the freedom of navigation and overflight enjoyed by all countries in accordance with international law, and safeguarding the safety of sea lanes.
Solving the Taiwan Province question and realizing the complete reunification of the country are the fundamental interests of the Chinese nation and the inevitable requirement for realizing the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation. China adheres to the principle of "peaceful reunification and one country, two systems", promotes the peaceful development of cross-strait relations and the process of China’s peaceful reunification, and resolutely opposes all attempts and acts to split China and any foreign interference. China must and must be unified. China has firm determination and strong ability to safeguard national sovereignty and territorial integrity, and will never allow anyone, any organization or any political party to split any piece of China territory from China at any time and in any form. We don’t promise to give up the use of force, but reserve the option of taking all necessary measures. We are targeting at the interference of external forces and a handful of "Taiwan independence" separatists and their separatist activities, and we are definitely not targeting Taiwan Province compatriots. If someone wants to split Taiwan Province from China, China’s army will resolutely defeat it at all costs and defend national unity.
Insist on never seeking hegemony, never expanding and never seeking sphere of influence.
This is a distinctive feature of China’s national defense in the new era.
Although the country is big, belligerence will die. The Chinese nation has always loved peace. In modern times, the people of China have suffered from aggression and war. They deeply feel the preciousness of peace and the urgency of development, and they will never impose their tragic experiences on others. In the 70 years since the founding of New China, China has never initiated any war or conflict. Since the reform and opening-up, China has devoted itself to promoting world peace and has taken the initiative to reduce the number of military personnel by more than 4 million. China’s development from poverty to weakness into the second largest economy in the world is not due to charity from others, let alone military expansion and colonial plunder, but to the hard work of the people and the maintenance of peace. China not only creates favorable conditions for its own development by safeguarding world peace, but also promotes world peace through its own development. It sincerely hopes that all countries will choose the path of peaceful development and jointly prevent conflicts and wars.
China insists on developing friendly cooperation with other countries on the basis of the Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence, respects the right of people of all countries to choose their own development path, advocates solving international disputes through equal dialogue, negotiation and consultation, and opposes interference in other countries’ internal affairs, bullying and imposing their will on others. China insists on partnership and non-alignment, does not join any military group, opposes aggression and expansion, and opposes the frequent use or threat of force. China’s national defense construction and development has always focused on meeting the legitimate needs of its own security and has always been the growth of world peace forces. History has proved, and will continue to prove, that China will never follow the old road of pursuing hegemony and "national power will dominate". No matter where it develops in the future, China will not threaten anyone and will not seek to establish a sphere of influence.
Implement the military strategic policy in the new era
This is the strategic guidance for China’s national defense in the new era.
The military strategic policy in the new era adheres to the principles of defense, self-defense and taking the initiative after the enemy strikes, implements active defense, adheres to the principle that "people will not attack me, and if they attack me, I will attack", and emphasizes the unity of containing wars and winning wars, and emphasizes the unity of strategic defense and offensive in campaigns and battles.
Implement the military strategic policy in the new era, obey the overall strategic situation of serving the party and the country, implement the overall national security concept, strengthen the sense of hardship, crisis and war, actively adapt to the new pattern of strategic competition, the new demand of national security and the new form of modern warfare, and effectively fulfill the military mission and tasks in the new era. According to the security threats facing the country, we should make solid preparations for military struggle, comprehensively improve the ability to prepare for war in the new era, and build a balanced and stable military strategic layout in the new era based on defense, multi-domain planning. Adhere to the national defense of the whole people, innovate the strategy, tactics and content of the people’s war, and give full play to the overall power of the people’s war.
China has always pursued a nuclear policy of not being the first to use nuclear weapons at any time and under any circumstances, and unconditionally not using or threatening to use nuclear weapons against non-nuclear-weapon States and nuclear-weapon-free zones. It advocates the ultimate complete prohibition and thorough destruction of nuclear weapons, will not engage in a nuclear arms race with any country, and will always maintain its nuclear power at the lowest level required by national security. China adheres to the strategy of self-defense and nuclear defense, with the aim of deterring other countries from using or threatening to use nuclear weapons against China and ensuring national strategic security.
Adhere to the road of strengthening the army with China characteristics
This is the development path of China’s national defense in the new era.
Building a strong national defense and a strong army commensurate with international status and national security and development interests is the strategic task of China’s socialist modernization, the security guarantee for adhering to the road of peaceful development and the inevitable choice for summing up historical experience.
In the new era, China’s national defense and army building will thoroughly implement the supreme leader’s military strategic thought, adhere to the political army building, reform and strengthen the army, strengthen the army through science and technology, and govern the army according to law, focus on fighting and winning battles, promote the integration and development of mechanization and informationization, accelerate the development of military intelligence, build a modern military force system with China characteristics, improve and develop Socialism with Chinese characteristics’s military system, and constantly improve its ability to fulfill its mission in the new era.
In the new era, the strategic goal of China’s national defense and army building is to basically realize mechanization by 2020, make significant progress in information construction, and greatly enhance its strategic capabilities. In line with the process of national modernization, we will comprehensively promote the modernization of military theory, military organization, military personnel and weapons and equipment, strive to basically realize the modernization of national defense and the army by 2035, and build the people’s army into a world-class army in an all-round way by the middle of this century.
Serve and build a community of human destiny
This is the world significance of China’s national defense in the new era.
The dreams of the people of China are closely linked with those of the people of the world. A peaceful, stable and prosperous China is an opportunity and a blessing for the world. A strong China army is a staunch force for maintaining world peace and stability and serving to build a community of human destiny.
China’s armed forces adhere to the common, comprehensive, cooperative and sustainable security concept, uphold the correct concept of justice and interests, actively participate in the reform of the global security governance system, deepen bilateral and multilateral security cooperation, promote coordination, tolerance and complementary cooperation among different security mechanisms, and create a security pattern of equality, mutual trust, fairness and justice, and joint construction and sharing.
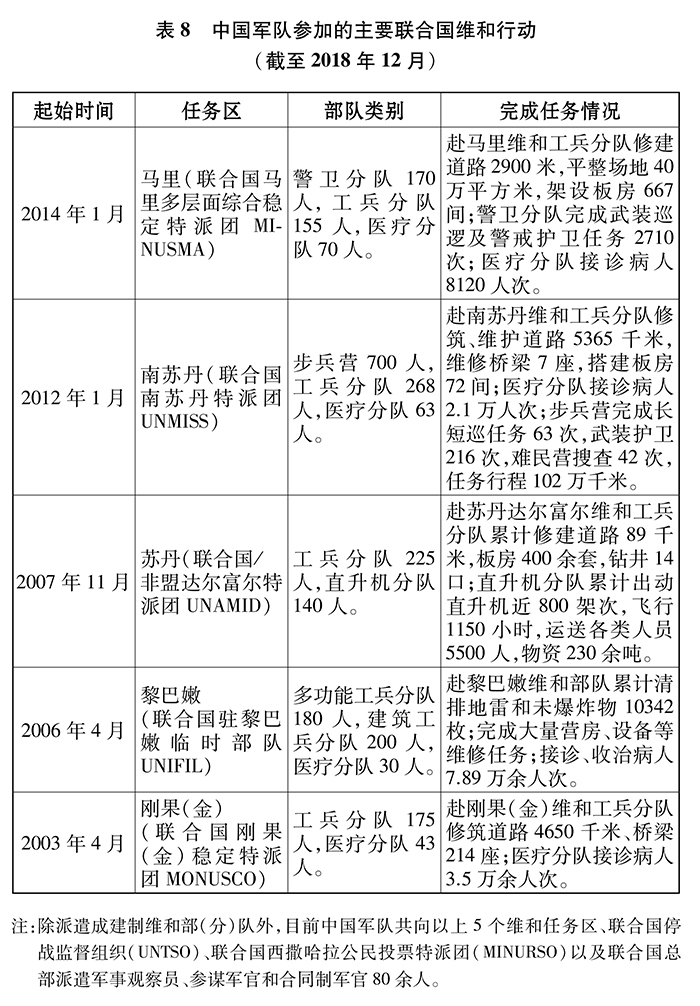
China’s military adheres to its international responsibilities and obligations, always holds high the banner of win-win cooperation, provides more public safety products to the international community within its capacity, actively participates in international peacekeeping, maritime escort, humanitarian relief and other actions, strengthens international arms control and non-proliferation cooperation, constructively participates in the political settlement of hot issues, jointly safeguards the safety of international passages, works together to meet global challenges such as terrorism, cyber security and major natural disasters, and actively contributes to building a community of human destiny.
Third, fulfill the mission of the army in the new era
In the new era, China’s army has resolutely fulfilled the mission entrusted by the Party and the people according to the strategic requirements of national security and development, and provided strategic support for consolidating the Communist Party of China (CPC)’s leadership and socialist system, defending national sovereignty, unity and territorial integrity, safeguarding national overseas interests and promoting world peace and development.
Safeguard the country’s territorial sovereignty and maritime rights and interests
With a land border of more than 22,000 kilometers and a coastline of more than 18,000 kilometers, China is one of the countries with the largest number of neighboring countries, the longest land border and a very complicated maritime security environment. The task of safeguarding territorial sovereignty, maritime rights and interests and national unity is arduous and arduous.
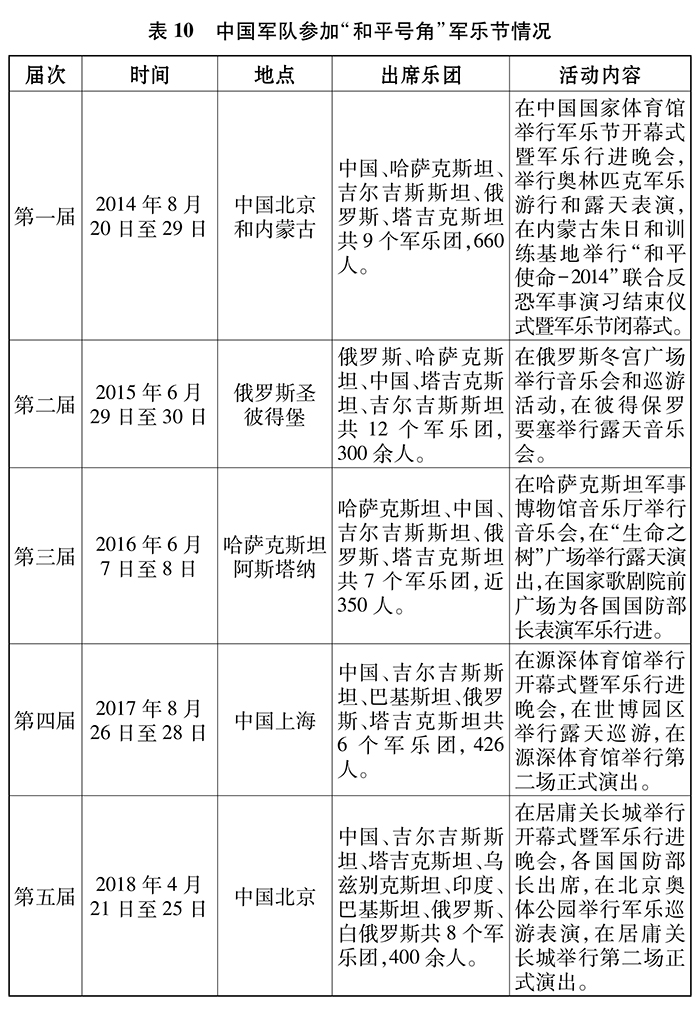
China’s armed forces strictly guard against all kinds of encroachment, infiltration, destruction and harassment activities, and safeguard the security and stability of border defense. China has signed border defense cooperation agreements with nine neighboring countries, established a meeting mechanism for border defense talks with 12 countries, established a three-level foreign exchange mechanism for the Ministry of National Defense, war zones and border defense forces, and regularly carried out friendly exchange visits, working talks, joint patrol duty and joint drills to combat cross-border crimes. Carry out border disarmament compliance with Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan. Strengthen the border defense in the direction of China and India, and take effective measures to create favorable conditions for the peaceful settlement of the confrontation between Dong Lang and Lang. Strengthen border control between China and Afghanistan to prevent the infiltration of terrorists. Strengthen security control in the direction of China and Myanmar, and maintain peace and people’s safety in border areas. Since 2012, China’s border guards have conducted more than 3,300 joint patrols and held more than 8,100 border defense meetings with neighboring countries. About 58 square kilometers of border mines have been cleared in the direction of China, Vietnam and Myanmar, and about 25 square kilometers of minefields have been enclosed, and about 170,000 explosives such as mines have been removed.
Organize the vigilance and defense of important sea areas and islands and reefs such as the East China Sea, the South China Sea and the Yellow Sea, grasp the surrounding maritime situation, organize joint maritime rights enforcement, properly handle the sea and air situation, and resolutely respond to maritime security threats and infringement and provocation. Since 2012, it has organized more than 4,600 patrols of ships and more than 72,000 law enforcement activities to safeguard peace and good order in the ocean.
Organize air defense and air reconnaissance and early warning, monitor the air dynamics in national airspace and surrounding areas, organize air police patrol and combat take-off, effectively deal with all kinds of air safety threats and emergencies, maintain air order and air defense safety.
With a view to safeguarding national unity, we should strengthen preparations for military struggle focusing on the maritime direction, organize ships and planes to "cruise around the island" and issue a solemn warning to the "Taiwan independence" separatist forces.
Maintain a constant state of readiness.
Keeping the army in combat readiness is an important guarantee for effectively responding to security threats and fulfilling its mission. The Central Military Commission and the theater joint operations command organization strictly implement the combat readiness duty system, regularly organize combat readiness inspection and combat readiness pull, maintain a state of readiness to fight, continuously improve the joint operations command capability, command and handle all kinds of emergencies safely and efficiently, and effectively carry out all kinds of urgent and dangerous tasks. In 2018, the Central Military Commission organized a surprise inspection of the whole army’s combat readiness and the promotion of the whole army, covering 21 provinces, autonomous regions, municipalities directly under the Central Government and parts of the East China Sea and South China Sea.
The People’s Liberation Army and the Armed Police Force strengthened the concept of combat readiness, strictly enforced the combat readiness system, strengthened combat readiness duty, carried out combat readiness drills in a down-to-earth manner, established a regular combat readiness order, maintained a good combat readiness state, and effectively carried out combat readiness (combat) duty, patrol duty and other tasks.
Carry out actual combat military training
Military training is the basic practical activity of the army in peacetime. China Army insists on putting military training in an important position, firmly establishing the only fundamental standard of combat effectiveness, perfecting the system of military training laws and standards, establishing and perfecting the training supervision system, organizing the military training supervision of the whole army for emergency response, implementing the responsibility system for training and preparing for war, carrying out mass training and competition activities, and constantly improving the level of actual combat training.
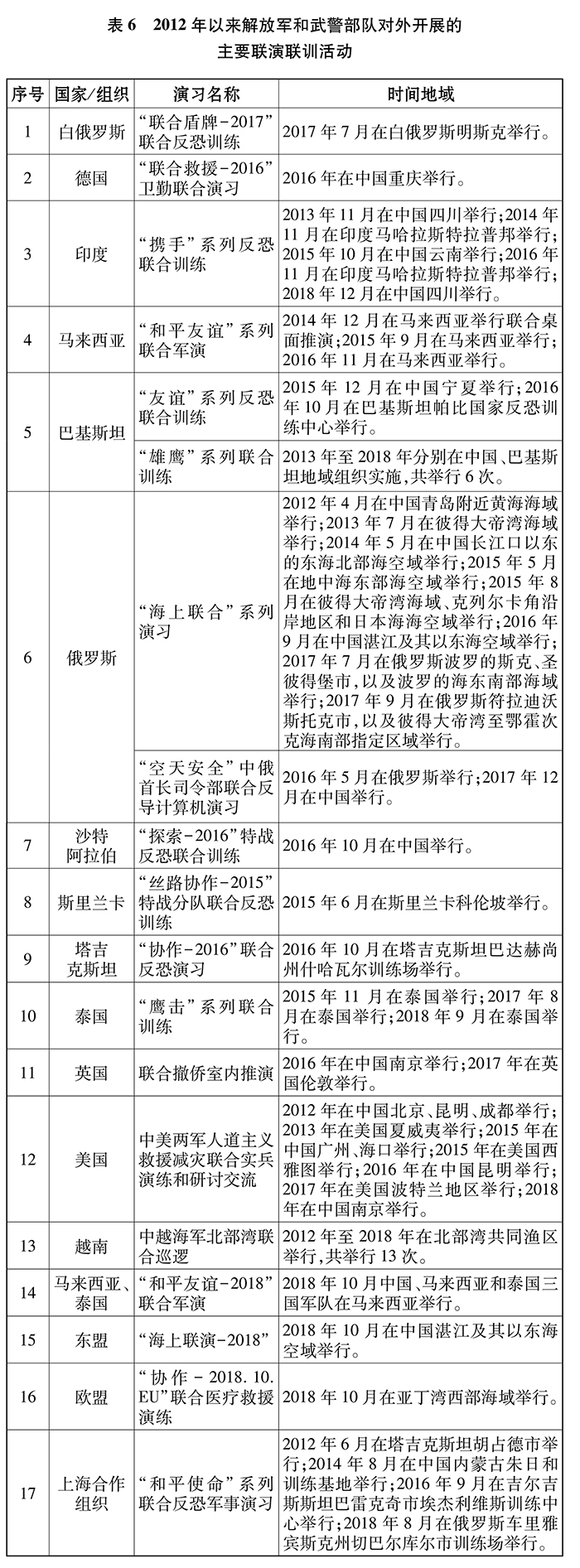
The whole army has risen to grasp the upsurge of actual combat military training. Since 2012, the whole army has extensively carried out targeted training on mission topics in various strategic directions and exercises of various arms and services, and more than 80 joint military exercises above the scale of divisions and brigades.
Each theater has strengthened the main responsibility of joint training, carried out joint training in a down-to-earth manner, and organized a series of joint military exercises in the East, the South, the West, the North and the Central in combination with the missions in various strategic directions, in an effort to improve the joint operational capability.
The army has conducted extensive military training contests and carried out live-fire exercises such as "crossing" and "firepower". The navy expanded its offshore training. For the first time, the aircraft carrier formation carried out offshore combat drills in the western Pacific Ocean, held maritime military parades in the South China Sea and the sea and airspace near Qingdao, and organized a series of "mobile" combat drills and systematic all-factor exercises. The Air Force has strengthened systematic and practical territory-wide training, organized war patrols in the South China Sea, police patrols in the East China Sea, and went out to the West Pacific before, and regularly carried out a series of system confrontation exercises such as "Red Sword". The Rocket Army organized confrontational inspection training, practical training for the whole brigade and regiment, strengthened joint fire strike training, and carried out a series of "Tianjian" exercises in a normal way. The strategic support forces actively integrated into the joint operational system and solidly carried out confrontation drills and emergency response training in new fields. The joint logistics support force promoted its integration into the joint combat system and organized a series of exercises such as "Joint Logistics Mission-2018". According to the requirements of covering the whole country, efficient linkage, global response and multi-function, the Armed Police Force has carried out a series of exercises such as "Guardian".
Safeguard the interests in major security fields
Nuclear power is the strategic cornerstone for safeguarding national sovereignty and security. China’s army strictly manages the safety of nuclear weapons and related facilities, maintains a moderate state of alert, improves its strategic deterrent capability, ensures national strategic security and maintains international strategic stability.
Space is the commanding height of international strategic competition, and space security is the strategic guarantee for national construction and social development. Focusing on the peaceful use of space, China actively participates in international space cooperation, speeds up the development of corresponding technologies and forces, manages space-based information resources as a whole, keeps track of the space situation, safeguards the safety of space assets, and improves its ability to enter and leave space safely and use space openly.
Cyberspace is a key area of national security and economic and social development. Network security is a global challenge and a severe security threat facing China. China’s army speeds up the construction of cyberspace forces, vigorously develops cyber security defense means, builds cyberspace defense forces commensurate with China’s international status and network power, builds up national cyber border defense, promptly discovers and resists network intrusion, ensures information network security, and resolutely defends national cyber sovereignty, information security and social stability.
Carry out anti-terrorism and stability
China resolutely opposes all forms of terrorism and extremism. Chinese armed forces take part in actions to maintain social order in accordance with the law, prevent and crack down on violent terrorist activities, safeguard national political security and overall social stability, and ensure the people live and work in peace and contentment.
The Armed Police Force carries out tasks such as guarding important targets, on-site guarding, setting up checkpoints on main roads and urban armed patrols, cooperates with state organs to participate in law enforcement actions according to law, cracks down on illegal criminal gangs and terrorist activities, actively participates in social prevention and control, and makes efforts to prevent and deal with all kinds of hidden dangers endangering national political security and social order, thus making important contributions to the construction of "Safe China". Since 2012, every year, a large number of troops have been deployed to undertake tasks such as duty security, counter-terrorism and maritime rights enforcement, and participated in nearly 10,000 security tasks such as the G20 Leaders’ Summit, the APEC Leaders’ Informal Meeting, the "Belt and Road" International Cooperation Summit Forum, the BRICS Leaders’ Meeting and the Qingdao Summit of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, and participated in the handling of 671 hostage-taking incidents and serious violent terrorist incidents. Since 2014, it has assisted the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region government in destroying 1,588 violent terrorist groups and arresting 12,995 violent terrorists.
The People’s Liberation Army assists local governments in maintaining social stability, participates in major security operations and handles other emergencies according to law, and mainly undertakes tasks such as preventing terrorist activities, nuclear and biochemical tests, medical rescue, transportation security, eliminating hidden dangers in water areas, and safeguarding air safety in places where major events are held and surrounding areas.
Safeguard overseas interests
Overseas interests are an important part of China’s national interests. Effectively safeguarding the security and legitimate rights and interests of overseas citizens, organizations and institutions in China is the task of the China Army.
China’s armed forces actively promote international security and military cooperation, and improve the mechanism for protecting overseas interests. Focus on bridging the gap between overseas operations and support capabilities, develop ocean-going forces, build overseas supply points, and enhance the ability to carry out diversified military missions. Carry out maritime escort, maintain the safety of strategic maritime passage, and then carry out overseas evacuation and maritime rights protection.
In August 2017, the Chinese People’s Liberation Army Support Base in Djibouti was officially put into use. Since the opening of the camp, it has provided maintenance equipment for four batches of escort formations, provided medical support services for more than 100 escort officers and soldiers, conducted joint medical rescue drills with foreign troops, and donated more than 600 pieces of teaching equipment to local schools.
In March, 2015, the security situation in Yemen deteriorated seriously. The China naval escort formation went to the Gulf of Aden, Yemen, and for the first time directly berthed at the ports in the war zone, and safely evacuated 621 citizens from China and 279 citizens from 15 countries including Pakistan, Ethiopia, Singapore, Italy, Poland, Germany, Canada, Britain, India and Japan.
Participate in emergency rescue and disaster relief
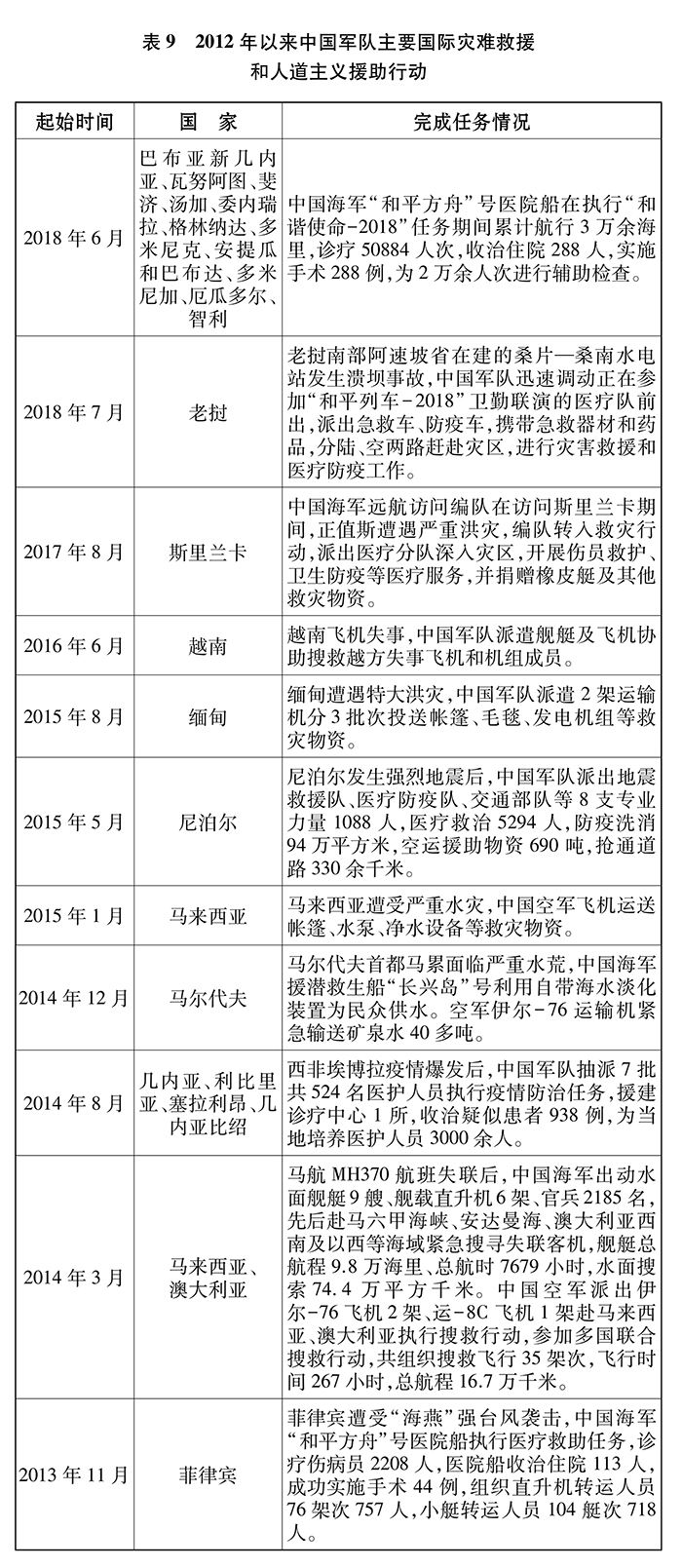
Participating in national construction and defending the people’s peaceful labor is the mission entrusted to the Chinese armed forces by the Constitution. According to the Regulations on Military Participation in Emergency Rescue and Disaster Relief, the Chinese armed forces are mainly responsible for rescuing, transferring or evacuating people trapped, protecting the safety of important targets, rescuing and transporting important materials, participating in professional emergency rescue such as road (bridge and tunnel) emergency repair, maritime search and rescue, nuclear and biochemical rescue, epidemic control and medical rescue, eliminating or controlling other critical dangers and disasters, and assisting local people’s governments in post-disaster reconstruction.
Since 2012, the People’s Liberation Army and the Armed Police Force have dispatched 950,000 person-times, organized 1.41 million militiamen, used 190,000 vehicles and construction machinery, 26,000 boats and 820 aircraft (helicopters) to participate in rescue and disaster relief. He has participated in disaster relief operations such as the earthquake relief in Ludian, Yunnan, the flood fighting in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, and the rescue of the Yarlung Zangbo River dammed lake, assisting local governments to rescue, transfer and resettle more than 5 million people, making rounds to treat more than 210,000 patients, rushing to transport more than 360,000 tons of materials, and strengthening more than 3,600 kilometers of dams. In 2017, the troops stationed in Macao dispatched 2,631 troops and more than 160 vehicles to assist the government of the Special Administrative Region to carry out rescue after the typhoon "Tiange".
Fourth, China’s national defense and army in reform.
The development history of the people’s army is a history of reform and innovation. Entering a new era, adapting to the development trend of the new military revolution in the world and the demand of national security, China has comprehensively promoted the modernization of national defense and the armed forces, comprehensively deepened the reform of national defense and the armed forces, made great efforts to solve institutional obstacles, structural contradictions and policy issues, and made a historic step of strengthening and rejuvenating the armed forces.
Rebuild the leadership and command system
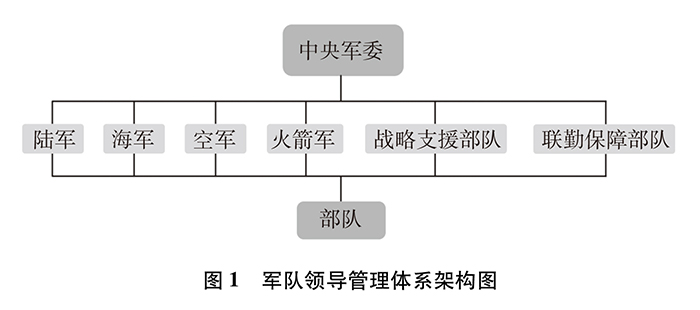
The reform of leadership and command system is an important measure to adapt to the requirements of modern military specialization and information age to fight and win battles, and to improve the operational efficiency and construction efficiency of the army. In accordance with the principle of "the military commission is in charge of the general affairs, the main battle of the theater and the main construction of the service", we will strengthen the functions of centralized and unified leadership, strategic command and strategic management of the military commission, break the long-standing headquarters system, the military region system and the continental army system, and build a new military leadership management and operational command system.
Adjust and form new organs and departments of the Central Military Commission. Optimize the functional allocation and institutional setup of the organs of the Military Commission, and adjust them from the past four headquarters of the General Staff Department, the General Political Department, the General Logistics Department and the General Armament Department to 15 functional departments of the organs of the Military Commission, serving as the staff organs, executive organs and service organs under the centralized leadership of the Military Commission. The path of command, construction, management and supervision is clearer, and the allocation of functions such as decision-making, planning, implementation and evaluation is more reasonable.
Improve the leadership and management system of services and arms. Integrate the army building functions of the original four headquarters and set up the army leading body; Integrate the strategic support forces of various services and military commissions and establish strategic support forces; The Second Artillery Corps was renamed Rocket Corps; Integrate the strategic campaign forces that mainly undertake general support tasks, set up joint logistics support forces, and build a leadership and management system of "Central Military Commission-services-troops".
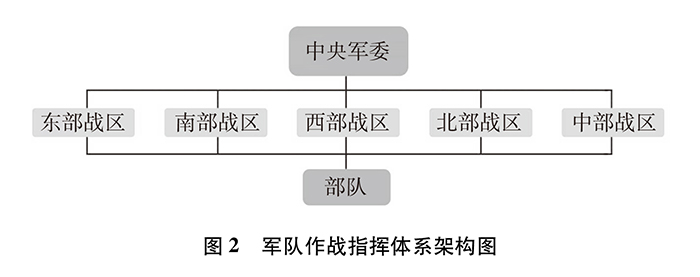
Establish and improve the joint operational command system. We will improve the joint operational command organization of the Central Military Commission and set up a joint operational command organization in a theater to form a joint operational command system that integrates peacetime and wartime, operates normally, specializes in the main business, and is lean and efficient. Seven major military regions in Shenyang, Beijing, Lanzhou, Jinan, Nanjing, Guangzhou and Chengdu were abolished, and five war zones in the east, south, west, north and central regions were established. Through reform, the operational command system of "Central Military Commission-Theater-Army" has been established.
Establish and improve the supervision system of rule of law. Set up a new Military Commission Discipline Inspection Committee (Military Commission Supervision Committee), under the direct leadership of the Central Military Commission, and send discipline inspection teams to the organs and departments of the Military Commission and various war zones; Establish a new Political and Legal Committee of the Military Commission, and set up military courts and military procuratorates according to regions; Set up the Audit Office of the Central Military Commission, reform the audit supervision system, and all of them will be stationed for auditing, thus forming a power operation system in which decision-making power, execution power and supervision power are mutually restricted and coordinated.
Optimize the scale structure and strength compilation
The reform of scale structure and strength organization is a key step to promote the modernization of military organization and build a modern military strength system with China characteristics. In accordance with the requirements of adjusting and optimizing the structure, developing new forces, rationalizing major proportional relations, and reducing quantity and scale, we will promote the transformation of the army from quantity-scale to quality-efficiency, manpower-intensive to technology-intensive
Adjust the proportion of military scale and reshape the layout of power structure. 300,000 military posts will be reduced, and the total number of active posts will be reduced to 2 million. Expand the allocation scope of non-commissioned officers and civilian personnel, reduce the establishment of organs at all levels, reduce the internal institutions, leadership levels and personnel of organs at all levels, streamline the press and publication of literature, art and sports, service guarantee, institutions and personnel such as colleges, medical institutions, warehouses and scientific research institutes, reduce the staff of organs at or above the regimental level by about a quarter, and reduce the staff of non-combat units by nearly half. Significantly reduce the number of active posts in the army, keep the number of active posts in the air force stable, moderately increase the number of active posts in the navy and rocket army, and optimize the internal strength structure of various services and arms. Optimize the structure of reserve forces. Adjust the deployment of combat forces and form a strategic layout that is compatible with the need to safeguard national security in the new era.
Adjust the formation of combat troops and reconstruct new combat forces. The original 18 army groups of the Army were integrated and reorganized into 13 army groups. The "Army-Brigade-Battalion" system is implemented in the main combat troops of the whole army, which enriches the combat strength of arms, reduces the command level and lowers the synthetic center of gravity. Increase new combat forces such as special operations, three-dimensional attack and defense, amphibious operations, offshore defense, strategic delivery, etc., and promote the development of troops in the direction of enrichment, synthesis, versatility and flexibility.
Optimize the strength distribution of colleges and universities and reconstruct the military scientific research system. The original 77 colleges and universities of the People’s Liberation Army and the Armed Police Force were integrated into 44, reshaping the National Defense University and the National University of Defense Technology. Establish the Military Scientific Research Steering Committee of the CMC, adjust and set up new Academy of Military Sciences and Service Research Institute, and form the layout of military scientific research forces with Academy of Military Sciences as the leader, scientific research institutions of services and arms as the backbone, and scientific research forces of colleges and troops as the auxiliary.
Promote the reform of the military policy system
Adhere to the standard of combat effectiveness, focus on mobilizing the enthusiasm, initiative and creativity of military personnel, design and promote the reform of military policy system as a whole, and establish and improve Socialism with Chinese characteristics’s military policy system.
Deepen the reform of the party building system in the army, safeguard the authority of the Party Central Committee and centralize and unify leadership, and ensure the party’s absolute leadership over the army. Formulate the "Decision on Strengthening Party Building in the Army in the New Era" and other laws and regulations, and promote the improvement of the political, ideological, organizational, work style and discipline construction systems of the military party.
Innovate the policy system for the use of military forces to effectively guarantee the full implementation of military missions and tasks in the new era. Formulate the Regulations on Maritime Escort Action (Trial) and other laws and regulations, and promote the improvement of the military strategic guidance system, combat readiness regulations, and joint operations regulations.
Rebuild the policy system of military strength construction and better liberate and develop combat effectiveness. Formulate and revise the National Defense Traffic Law, the Military Facilities Protection Law, the Civilian Personnel Regulations and other laws and regulations, and promulgate and implement new military training regulations and military training programs. We will promote the establishment of a professional system for military officers, optimize the protection of military treatment, improve the honor system for military personnel, improve policy systems in military training, equipment development, logistics construction, military scientific research, and national defense mobilization, and accelerate the legislative process of the military officer law and military service law.
Reform the military management policy system, improve the operational efficiency of the military system, and promote the high-quality development of the military. Formulate and revise the internal affairs regulations (for Trial Implementation), discipline regulations (for Trial Implementation), queue regulations (for Trial Implementation), and regulations on military legislation, and promote institutional innovations such as strategic management, military expenditure management, and military justice.
Completely stop the paid service of the army. By June 2018, paid service activities in 15 industries, such as real estate leasing, agricultural and sideline production, recruitment and reception, which were engaged in by military organs, troops at all levels and their affiliated institutions, had basically stopped, and more than 100,000 paid service projects had been stopped on schedule, and the cumulative proportion of paid projects had reached 94%, and the goal of the military not engaging in business activities had basically been achieved.
Adjust the reformed services and armed police forces.
The army plays an irreplaceable role in safeguarding national sovereignty, security and development interests. Including mobile combat troops, border and coastal defense forces, security forces, etc., it has jurisdiction over five war zones, the Army, the Xinjiang Military Region and the Tibet Military Region. The Army of the Eastern Theater has the 71st, 72nd and 73rd Army, the Army of the Southern Theater has the 74th and 75th Army, the Army of the Western Theater has the 76th and 77th Army, the Army of the Northern Theater has the 78th, 79th and 80th Army, and the Army of the Central Theater has the 81st, 82nd and 83rd Army. In accordance with the strategic requirements of mobile operations and three-dimensional attack and defense, we will accelerate the transformation from regional defense to global operations, improve the capabilities of precision operations, three-dimensional operations, global operations, multi-energy operations and sustained operations, and strive to build a powerful modern new army.
The navy plays a very important role in national security and overall development. Including submarine forces, surface warships, aviation, marine corps, coastal defense forces, etc., it has jurisdiction over the Eastern Theater Navy (East China Sea Fleet), the Southern Theater Navy (South China Sea Fleet), the Northern Theater Navy (North Sea Fleet), and the Marine Corps. Battlefield naval bases, submarine detachments, surface ship detachments, aviation brigades and other units. In accordance with the strategic requirements of offshore defense and offshore defense, we will accelerate the transformation from offshore defense to offshore defense, improve strategic deterrence and counterattack, maritime mobile operations, maritime joint operations, comprehensive defense operations and comprehensive support capabilities, and strive to build a powerful modern navy.
The air force plays an important role in national security and overall military strategy. Including aviation, airborne troops, ground air defense troops, radar troops, electronic countermeasures troops, information and communication troops, etc., it has five theater air forces and one airborne army. Theater Air Force has bases, aviation brigades (divisions), ground-to-air missile troops brigades (divisions), radar brigades and other units. In accordance with the strategic requirements of air and space integration and both attack and defense, we will accelerate the transformation from national air defense to both attack and defense, improve the capabilities of strategic early warning, air strike, air defense and anti-missile, information countermeasure, airborne combat, strategic delivery and comprehensive support, and strive to build a powerful modern air force.
The rocket army plays a vital role in safeguarding national sovereignty and security. Including nuclear missile forces, conventional missile forces, support forces, and missile bases under its jurisdiction. In accordance with the strategic requirements of both nuclear and conventional capabilities and global deterrence, we will enhance credible and reliable nuclear deterrence and nuclear counterattack capabilities, strengthen the construction of medium-and long-range precision strike forces, enhance strategic checks and balances, and strive to build a powerful modern rocket army.
The strategic support force is a new type of combat force to safeguard national security and an important growth point of new combat capability. Including battlefield environment guarantee, information communication guarantee, information security protection, new technology test and other support forces. In accordance with the system integration and the strategic requirements of integration of defense and civilian technologies, we will promote the leap-forward development of key areas, accelerate the development of new combat forces, and strive to build a powerful modern strategic support force.
Joint logistics support force is the main force to implement joint logistics support and strategic campaign support, and it is an important part of modern military force system with China characteristics. Including warehousing, medical service, transportation and delivery, oil pipelines, engineering construction management, reserve assets management, procurement and other forces, it has five joint logistics support centers in Wuxi, Guilin, Xining, Shenyang and Zhengzhou, as well as the PLA General Hospital and the PLA Center for Disease Control and Prevention. In accordance with the requirements of joint operations, joint training and joint support, we should speed up our integration into the joint operation system, improve the integrated joint support capability, and strive to build a powerful modern joint logistics support force.
The Armed Police Force shoulders great responsibilities in safeguarding national security and social stability and safeguarding people’s better life, and implements the leadership and command system of "Central Military Commission-Armed Police Force-Army". The fundamental functional attributes of the Armed Police Force have not changed and are not included in the PLA sequence. Public security frontier forces, public security fire fighting forces and public security guards were retired from active service, the marine police team led and managed by the State Oceanic Administration was transferred to the Armed Police Force, and the gold, forest and hydropower units of the Armed Police Force as a whole were transferred to relevant state functional departments and reorganized into non-active professional teams, and the customs duty forces of the Armed Police Force were withdrawn, completely rationalizing the relationship between leadership, management and command and use of the Armed Police Force. After the adjustment, the armed police force includes internal security forces, mobile forces and marine police forces. In accordance with the strategic requirements of multi-functional integration and effective stability, we will strengthen the capacity building of duty, handling emergencies, counter-terrorism, maritime rights protection and administrative law enforcement, emergency rescue, and strive to build a powerful modern armed police force.
Promote the all-round construction of national defense and the army
Always put ideological and political construction in the first place in all aspects of military construction. Firmly establish the guiding position of the supreme leader’s thought of strengthening the army, resolutely safeguard the core position of the CPC Central Committee and the whole party, resolutely safeguard the authority of the CPC Central Committee and centralize and unify leadership, implement the responsibility system for the chairman of the Central Military Commission, and further enhance political awareness, overall situation awareness, core awareness and conformity awareness. In December 2014, the "Decision on Several Issues in Military Political Work under the New Situation" was issued to promote political consolidation and training, and the army reorganized its luggage and set out again. In August 2018, a party building meeting of the Central Military Commission was held to comprehensively strengthen the leadership and party building of the military in the new era. Efforts will be made to cultivate revolutionary soldiers with soul, ability, blood and morality in the new era, and forge excellent troops with iron general beliefs, iron general beliefs, iron general discipline and iron general responsibility.
Promote the innovation and development of national defense science and technology and military theory. We will speed up the implementation of the strategy of developing the army through science and technology, consolidate and strengthen advantageous fields, and intensify innovation in emerging fields. Some strategic, cutting-edge and subversive technologies have made important progress in independent innovation, and a number of high-tech achievements such as Tianhe-2 supercomputer have been successfully developed. Focus on war and combat issues to promote military theoretical innovation, and launch a series of theoretical achievements such as strategy, joint operations, and information construction to provide theoretical support for national defense and army building.
Build a modern weapon and equipment system. Improve and optimize the system structure of weapons and equipment, promote the development of weapons and equipment of all services and arms as a whole, coordinate the development of main battle equipment, information systems and support equipment, and comprehensively improve the level of standardization, serialization and generalization. Intensify the elimination of old equipment and gradually form a weapon and equipment system with high-tech equipment as the backbone. Type 15 tanks, 052D destroyers, J-20 fighters, Dongfeng-26 medium-and long-range ballistic missiles and other equipment are installed.
Build all modern logistics for war. We will establish a support system with the joint logistics department as the mainstay, the services as the supplement, the combination of unification and separation, and the integration of expertise. We will build a joint, lean and efficient logistics force system with strategic campaign forces as the mainstay, team-owned forces as the supplement, and social security as the support. We will promote the integration of logistics forces into joint training in war zones, cross-regional training of services and arms, and joint training of Chinese and foreign outreach, and promote the integration of front and rear training, initially forming the ability of rapid response, all-round participation in war and accurate support.
Strengthen strategic management. Adhere to demand-driven planning, planning leading resource allocation, and establish and improve the strategic management link of "demand-planning-budget-implementation-evaluation". Formulate military development strategies and development strategies for important areas, services and arms, and armed police forces, and form a strategic planning and planning system. Standardize the strategic planning of the armed forces, promulgate and implement the Outline of the 13th Five-Year Plan for the Construction and Development of the Armed Forces, and improve the system and mechanism of evaluation, supervision and regulation.
坚持依法治军从严治军。构建完善中国特色军事法治体系,推动治军方式根本性转变。强化练兵备战监督监察,深入纠治和平积弊。广泛开展法治宣传教育,建立健全法律咨询服务保障机制,推进法治军营建设。全面从严加强部队管理,贯彻落实条令条例,恢复和完善军队司号制度,组织全军安全大检查,加强重大安全隐患排查整治,加大警备纠察工作力度,开展军车管理专项整顿,建立警备工作定期通报机制,维护军队良好形象。
深入推进党风廉政建设和反腐败斗争。严明政治纪律政治规矩,严肃查处郭伯雄、徐才厚、房峰辉、张阳等严重违纪违法案件。严格依纪依法惩治腐败,开展重大工程建设、装备物资采购等行业领域专项整治。建立基层风气监察联系点制度,查纠官兵身边“微腐败”和不正之风。深化政治巡视,完成对军委机关部门、大单位巡视和回访巡视全覆盖。着力推进审计全覆盖,加大重点领域、重大项目、重要资金审计力度,严格领导干部经济责任审计,积极推行经费绩效审计、全程跟踪审计、军地联合审计。2012年以来,共审计3.9万个(次)单位(部门)、1.3万名团以上领导干部。反腐败斗争取得压倒性胜利,风清气正的良好政治生态基本形成。
Promote the modernization of national defense mobilization. Straighten out the leadership system of national defense mobilization organizations, strengthen the construction of reserve forces, streamline the scale of the national backbone militia, deepen the reform of the scale structure and strength of the militia reserve forces, promote the integrated construction and application of reserve forces and active forces, and accelerate the transformation from ensuring the army as the mainstay to ensuring multiple services and arms.
In combination with deepening the reform of the party and state institutions, the Department of Veterans Affairs was established to promote the construction of the service guarantee system for veterans in provinces, cities, counties, towns (streets) and villages (communities), and a series of preferential treatment measures were introduced. Solidly do a good job in supporting the army and its dependents, supporting the government and loving the people, actively participate in poverty alleviation, continuously consolidate the unity between the military, the government and the people, and form a social atmosphere of respecting and giving preferential treatment to soldiers.
V. Reasonable and moderate defense expenditure
China adheres to the balance between development and security, the unification of enriching the country and strengthening the army, the coordinated development of national defense construction and economic construction, the policy of building the army through diligence and thrift, reasonably determining the scale structure of defense expenditure according to the country’s economic development level and national defense demand, and managing and using defense expenditure according to law.
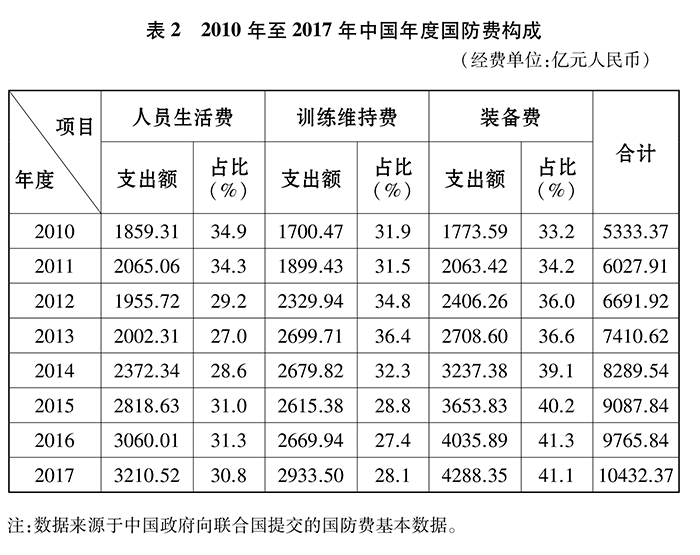
Since the reform and opening-up, China’s national defense expenditure has experienced a development process from maintenance investment to moderate growth, and generally maintained a moderate and coordinated growth in step with the national economic and financial expenditure. The proportion of defense expenditure in gross domestic product (GDP) dropped from the highest 5.43% in 1979 to 1.26% in 2017, and remained within 2% for nearly 30 years. In 1979, defense expenditure accounted for 17.37% of the national fiscal expenditure, and in 2017 it was 5.14%, a decrease of more than 12 percentage points, and the overall downward trend was obvious.
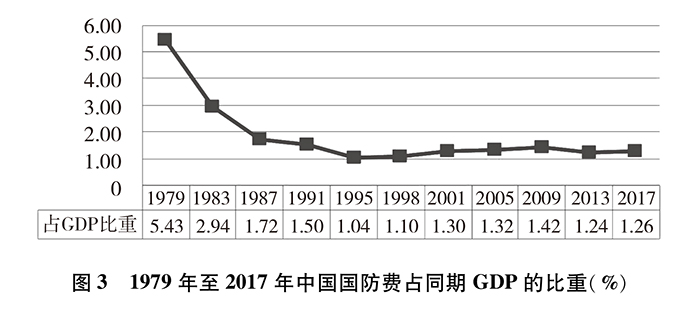
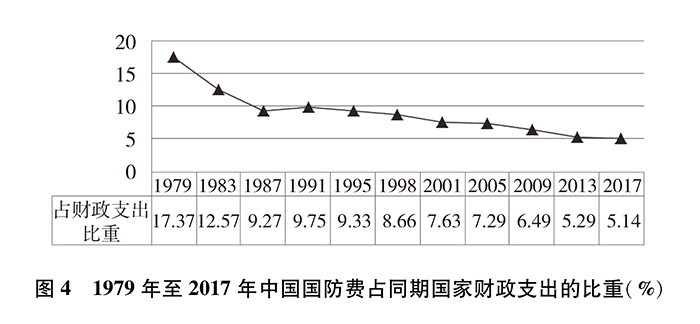
In the new era, in line with the process of national modernization, with the focus on building a consolidated national defense and a strong army commensurate with China’s international status and national security and development interests, further narrowing the gap with the world’s advanced military level, and solving the problem of the army’s insufficient ability to fight modern wars, China’s defense expenditure scale has maintained a steady growth, and its expenditure structure has been continuously optimized.
China’s defense expenditure is divided by purpose, mainly consisting of personnel’s living expenses, training maintenance expenses and equipment expenses. Personnel living expenses are used for salaries, allowances, meals, clothing, insurance, welfare and pensions of officers, civilian cadres, soldiers and employed non-active personnel, as well as retired cadres supported by the army. Training maintenance expenses are used for military training, college education, construction and maintenance of engineering facilities and other daily consumption expenses. Equipment costs are spent on research, testing, procurement, maintenance, transportation and storage of weapons and equipment. The scope of defense expenditure includes active troops, reserve troops and militia.
The increase in defense expenditure since 2012 is mainly used for: (1) adapting to the country’s economic and social development, improving the living and welfare benefits of officers and men, implementing the mechanism of regular wage increase for military personnel, and continuously improving the working, training and living security conditions of grass-roots units. (2) Increase investment in weapons and equipment construction, eliminate and update some backward equipment, upgrade some old equipment, research and purchase new weapons and equipment such as aircraft carriers, combat aircraft, missiles and main battle tanks, and steadily improve the modernization level of weapons and equipment. (3) Deepen the reform of national defense and the army, and ensure major reforms such as the leadership and command system of the army, the size structure and strength of the army, and the military policy system. (4) Ensure actual combat training, strategic training, joint training in war zones, and training in services and arms, and strengthen the construction of simulated, networked and confrontational training conditions. (5) Ensuring diversified military tasks and ensuring international peacekeeping, escort, humanitarian rescue, emergency rescue and disaster relief.
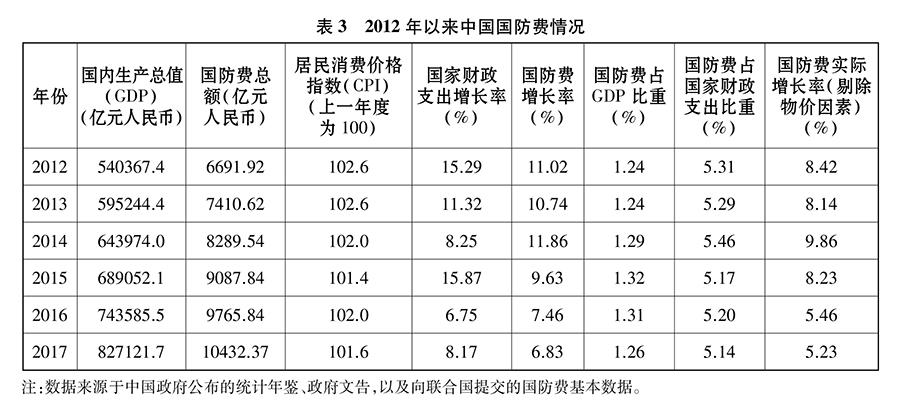
From 2012 to 2017, China’s defense expenditure increased from 669.192 billion yuan to 1,043.237 billion yuan. China’s gross domestic product (GDP) increased by 9.04% at the current price, the national fiscal expenditure increased by 10.43%, the defense expenditure increased by 9.42%, and the defense expenditure accounted for 1.28% of the GDP and 5.26% of the national fiscal expenditure. The proportion of defense expenditure in GDP is stable, and it keeps pace with the national financial expenditure.
China implements strict financial allocation and budget management system for defense expenditure. The use of defense expenditure should be guided by demand and planning; we should live within our means; we should strengthen centralized and unified management; we should make overall plans for the incremental stock; we should gradually implement performance management of defense expenditure; and we should promote the reform of military expenditure management with efficiency as the core. Improve and strengthen budget management, deepen the reform of centralized payment and receipt system of military funds, speed up the pace of standardization of funds, and improve the management methods of military assets and funds.
International comparison of defense expenditure
Among the countries with the highest defense expenditure in the world in 2017, China’s defense expenditure is at a low level in terms of the proportion of GDP and national fiscal expenditure, as well as the per capita national and military figures.
China has become the second largest economy in the world. The scale of national defense expenditure ranks second in the world, which is determined by China’s national defense demand, economic volume and defensive national defense policy. In terms of total expenditure, China’s defense expenditure in 2017 was less than a quarter of that of the United States.
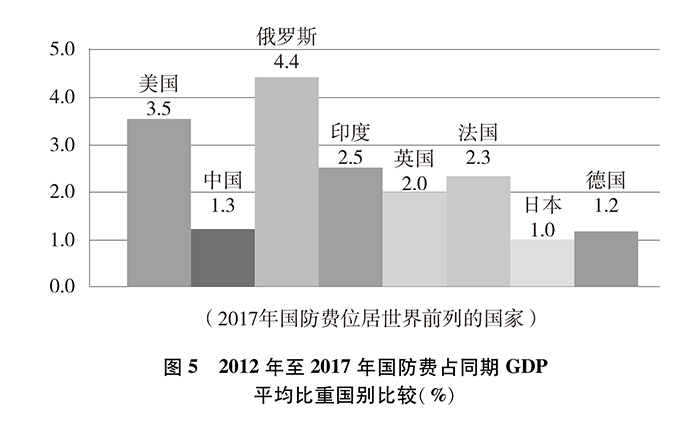
In terms of the proportion of defense expenditure in GDP, from 2012 to 2017, the average proportion of defense expenditure in GDP in China was about 1.3%, that in the United States was about 3.5%, that in Russia was about 4.4%, that in India was about 2.5%, that in Britain was about 2.0%, that in France was about 2.3%, that in Japan was about 1.0% and that in Germany was about 1.2%. The average proportion of China’s defense expenditure in GDP ranks sixth among the countries with the highest defense expenditure in the world and the lowest among the permanent members of the UN Security Council.
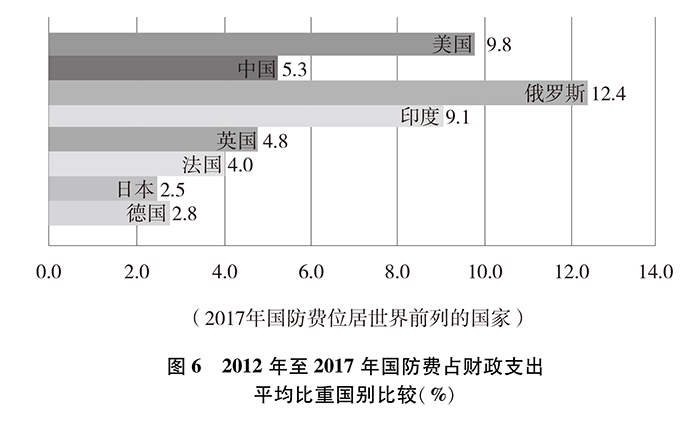
In terms of the proportion of defense expenditure in fiscal expenditure, from 2012 to 2017, the average proportion of defense expenditure in fiscal expenditure in China was about 5.3%, that in the United States was about 9.8%, that in Russia was about 12.4%, that in India was about 9.1%, that in Britain was about 4.8%, that in France was about 4.0%, that in Japan was about 2.5% and that in Germany was about 2.8%. China’s defense expenditure ranks fourth in the average proportion of fiscal expenditure.
From the level of per capita defense expenditure, in 2017, the per capita defense expenditure of China citizens was 750 yuan RMB, which was about 5% of that of the United States, 25% of that of Russia, 231% of that of India, 13% of that of Britain, 16% of that of France, 29% of that of Japan and 20% of that of Germany. China’s per capita defense expenditure is 521,600 yuan, which is about 15% of that of the United States, 119% of Russia, 166% of India, 27% of Britain, 38% of France, 35% of Japan and 30% of Germany. China ranks seventh in national defense expenditure per capita and sixth in military defense expenditure per capita.
China adheres to the system of reporting and publishing defense expenditure. Since 1978, the China Municipal Government has submitted a budget report to the National People’s Congress every year, and announced the total annual defense budget. In 1995, the Government of China issued a white paper entitled "Arms Control and Disarmament in China", which announced the defense expenditure to the world. Since 2007, China has participated in the United Nations military transparency system, and submitted the basic data of defense expenditure in the last fiscal year to the United Nations every year. According to the categories of active troops, reserve troops and militia, it submitted the amount of personnel’s living expenses, training maintenance expenses and equipment expenses, and the total defense expenditure, and explained the main purpose and proportion of China’s defense expenditure to GDP.
On the whole, China’s defense expenditure is open and transparent, and its expenditure level is reasonable and moderate. Compared with major countries in the world, the proportion of defense expenditure in GDP and fiscal expenditure and the per capita defense expenditure are low. China is the only big country in the world that has not yet achieved complete reunification, and it is one of the countries with the most complicated security situation around the world. It faces severe challenges in safeguarding national sovereignty, territorial integrity and maritime rights and interests. China is approaching the center of the world stage, and the international community’s expectations for China’s military to provide international public safety products are increasing. China’s army is in the stage of information transformation, and the task of adapting to the development trend of the new military revolution in the world and promoting military transformation with China characteristics is arduous and arduous. There is still a big gap between China’s national defense expenditure and the demand for safeguarding national sovereignty, security and development interests, and the demand for fulfilling the international responsibilities and obligations of big countries, and the demand for its own construction and development. China’s defense expenditure will be coordinated with the national economic development level and will continue to maintain moderate and steady growth.
Sixth, actively serve and build a community of human destiny
Building a community of human destiny conforms to the trend of peaceful development and reflects the common expectations of people of all countries. China’s armed forces faithfully practice the concept of a community of human destiny, actively fulfill the international responsibilities of big-country armed forces, comprehensively promote international military cooperation in the new era, and strive to contribute to building a beautiful world of lasting peace and universal security.
Firmly uphold the purposes and principles of the UN Charter.
As a founding member of the United Nations and a permanent member of the Security Council, China firmly upholds the central role of the United Nations in international affairs, international law and basic norms of international relations based on the purposes and principles of the Charter of the United Nations, multilateralism, democratization of international relations, extensive participation in global security governance, active participation in arms control and disarmament, and contribution to China’s plan for solving major problems and formulating important rules.
China constructively participates in the political settlement of hot issues in the region, such as the Korean Peninsula issue, the Iranian nuclear issue and the Syrian issue, opposes hegemonism, unilateralism and double standards, promotes dialogue and consultation, and fully and conscientiously implements UN Security Council resolutions. China actively participates in multilateral dialogues and negotiations in the fields of internet and outer space, and promotes the formulation of universally accepted, fair and reasonable international rules.
China has always actively participated in international arms control, disarmament and non-proliferation efforts, opposed the arms race and maintained global strategic balance and stability. It has signed or acceded to dozens of multilateral arms control, disarmament and non-proliferation treaties, including the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons. In 2015, China announced the establishment of the China-United Nations Peace and Development Fund with a total amount of US$ 1 billion for 10 years, which was officially put into operation in 2016.
Promote the construction of a new security partnership featuring equality, mutual trust and win-win cooperation.
China actively develops constructive military relations with foreign countries and forms a new pattern of all-round, wide-ranging and multi-level military diplomacy. So far, China has carried out military exchanges with more than 150 countries, set up 130 military attaché s abroad in embassies (missions), set up military attaché s offices in China in 116 countries, and established 54 defense consultation and dialogue mechanisms with 41 countries and international organizations. Since 2012, high-level military delegations of the China Army have visited more than 60 countries, and more than 100 national defense ministers and army commanders have visited.
The relationship between the Chinese and Russian armed forces continues to maintain a high level of operation, constantly enriching new connotations for the comprehensive strategic cooperative partnership between the two countries in the new era, and is of great significance to maintaining global strategic stability. The exchange mechanism between the Chinese and Russian armed forces at all levels has been continuously and healthily promoted, with in-depth cooperation in the fields of high-level exchanges, military training, equipment technology and counter-terrorism, and good interaction and cooperation in international multilateral occasions. Since 2012, the Chinese and Russian armed forces have held seven rounds of strategic consultations. From August to September, 2018, at the invitation of China, the Russian army participated in the Russian "Oriental" strategic exercise for the first time.
In accordance with the principles of non-conflict, non-confrontation, mutual respect and win-win cooperation, China actively and steadily handles its military relations with the United States, strives to make the relations between the two militaries a stabilizer for the relations between the two countries, and contributes to the promotion of Sino-US relations based on coordination, cooperation and stability. In 2014, the defense ministries of the two countries signed two memorandums of understanding, namely, the mechanism of mutual notification of trust measures for major military operations and the code of conduct for maritime and air encounters. In 2015, the two sides reached a consensus on adding the annexes of "military crisis notification" and "air encounters". In 2017, the two countries established diplomatic security dialogue and joint staff dialogue mechanisms to actively strengthen strategic communication and control risk differences. The two sides have carried out institutional exchanges in defense departments, army, navy and air force, and carried out pragmatic cooperation in the fields of humanitarian relief and disaster reduction, anti-piracy and exchanges between colleges and universities. China resolutely opposes the wrong practices and provocative actions of the United States, such as arms sales to Taiwan, sanctions against the Equipment Development Department of China’s Central Military Commission and the head of the department, trespassing into China’s territorial waters and the sea and airspace adjacent to relevant islands and reefs, and conducting large-scale high-intensity approach reconnaissance. In Sino-US relations, the relations between the two armies have remained generally stable.
China aims to build a community of peripheral destiny and deepen its military partnership with neighboring countries. Maintain close contacts with the top military officials of neighboring countries. Every year, there are more than 40 batches of delegations above the commander level, basically achieving full coverage of high-level exchanges around the country and continuously strengthening strategic mutual trust. Establish defense security consultation and working meeting mechanisms with 17 neighboring countries, and keep communication channels open. In recent years, China has regularly organized a series of joint exercises and trainings with neighboring countries on counter-terrorism, peacekeeping, rescue, services and tactics, and extensively carried out exchanges on border defense and coastal defense, think tanks in colleges and universities, education and training, medical treatment, equipment and technology, and deepened pragmatic cooperation. The level of defense cooperation with ASEAN has been continuously improved, and military relations with neighboring countries have been generally stable.
China has actively developed military relations with European countries, and maintained a positive development momentum in exchanges and cooperation in various fields. Focusing on building the four partnerships of peace, growth, reform and civilization between China and Europe, China held security policy dialogues, joint anti-piracy drills and personnel training with the EU. In 2016, China and the United Kingdom held a joint indoor deduction for evacuating overseas Chinese, and held a joint medical service exercise with Germany. In 2018, China and the EU held the third China-EU high-level security policy seminar.
China has strengthened military exchanges with developing countries in Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean, the South Pacific and other regions, conducted personnel training and exchanges between young and middle-aged officers, and helped the countries concerned to strengthen their army building and improve their defense capabilities. In 2018, China-Africa Defense Security Forum, China-Latin America Advanced Defense Forum and China-Canada (Lebi) South (Pacific) Advanced Defense Seminar were held in Beijing.
China’s armed forces adhere to the principle of mutual trust and mutual benefit, win-win cooperation and carry out pragmatic exchanges and cooperation with the armed forces of other countries. Since 2012, China has held more than 100 joint exercises and trainings with more than 30 countries. The content of the exercises has developed from the non-traditional security field to the traditional security field, the exercise area has extended from the periphery of China to the distant sea, and the participation strength has expanded from the army to the multi-arms of the army, navy and air force. China’s military actively organizes personnel training exchanges and cooperation. Since 2012, it has sent more than 1,700 military students to more than 50 countries, and more than 20 military academies have established and maintained inter-school exchange relations with universities in more than 40 countries, accepting tens of thousands of military personnel from more than 130 countries to study in China military academies.
Improve the military news release mechanism, and comprehensively and objectively introduce and explain China’s national defense and army building at home and abroad. In April 2011, the Ministry of National Defense established a monthly routine press conference system to regularly release important information on national defense and army building. Since 2012, a number of special press conferences have been held around major issues such as deepening national defense and military reform and reducing military posts. Organized nearly 100 Chinese and foreign media to visit and interview troops and military academies for many times. In May 2015, the official Weibo WeChat released by the Ministry of National Defense was officially launched, with more than 6 million followers.
Promote the construction of regional security cooperation framework
In June 2001, China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan jointly initiated the establishment of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. The Shanghai Cooperation Organization has become a comprehensive new regional cooperation organization with the widest territory and the largest population in the world. It has formed the "Shanghai Spirit" of mutual trust, mutual benefit, equality, consultation, respect for diverse civilizations and seeking common development, promoted the building of a community of destiny of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, promoted the building of new international relations, and made new contributions to regional peace and development. In June 2017, the Shanghai Cooperation Organization expanded its membership for the first time, and India and Pakistan became members of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. In April 2018, the first meeting of defense ministers after the expansion of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization was held. The member States of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization continue to strengthen exchanges and cooperation in the field of defense and security, hold a series of "Peace Mission" exercises, hold a "Horn of Peace" military music festival, deepen good-neighborly friendship and strategic mutual trust, strengthen military cultural exchanges, and enhance the unity and friendship of member States.
China actively supports the mechanism construction of the Conference on Mutual Cooperation and Confidence Measures in Asia, and advocates the establishment of a common, comprehensive, cooperative and sustainable Asian security concept, which has played an important role in building the security cooperation framework in Asia.
Based on the principle of openness, inclusiveness and pragmatic cooperation, China actively participated in multilateral dialogue and cooperation mechanisms such as the ASEAN Defense Ministers’ Enlargement Meeting, the ASEAN Regional Forum, the shangri-la dialogue Conference, the Jakarta International Defense Dialogue, and the Western Pacific Naval Forum, held informal China-ASEAN Defense Ministers’ meetings regularly, and constructively put forward initiatives to strengthen regional defense and security cooperation. In October 2018, the China-ASEAN "Joint Performance at Sea-2018" exercise was held, which was the first time that the armies of China and ASEAN countries held a maritime exercise, demonstrating the confidence and determination of China and ASEAN countries to maintain regional peace and stability.
China adheres to the spirit of equality, openness, tolerance and mutual learning, and builds the exchange platform of Beijing Xiangshan Forum. In 2014, Xiangshan Forum was upgraded to a "one track and a half" international security and defense dialogue platform. In October 2018, Xiangshan Forum was renamed Beijing Xiangshan Forum. More than 500 representatives from 67 countries and 7 international organizations attended the forum to discuss new ideas and new ways to deal with regional security threats and challenges, which played a positive role in promoting security dialogue and mutual trust and cooperation in the Asia-Pacific region.
Properly handle territorial issues and maritime delimitation disputes.
China adheres to the neighboring diplomatic concept of sincerity and tolerance, and persists in being a good neighbor and partner, and peacefully resolves territorial issues and maritime delimitation disputes through negotiation and consultation. China has settled land border issues with 12 of the 14 land neighbors, and signed treaties of good-neighborliness, friendship and cooperation with 8 neighboring countries.
China regards managing differences and enhancing mutual trust as an important part of maintaining stability in the surrounding areas, and proposes to set up a China-ASEAN defense chiefs hotline, establish direct telephone lines with Vietnam and South Korea respectively, and conduct regular or irregular telephone and fax contacts, border talks and meetings, joint patrols, etc. with the armies of countries bordering the land. Since 2014, China and Viet Nam have held five high-level border meetings. The Chinese and Indian armed forces have implemented the important consensus reached by the leaders of the two countries, conducted high-level visits and communication, and promoted the establishment of border hotline and border control and border exchange mechanisms. Since the second half of 2016, China and the Philippines have strengthened maritime security dialogue, and the two sides have returned to the correct track of handling the South China Sea issue through friendly consultations. In May 2018, the defense departments of China and Japan signed a memorandum on the air-sea liaison mechanism and started the operation of the mechanism in June.
China and ASEAN countries have fully and effectively implemented the Declaration on the Conduct of Parties in the South China Sea, actively promoted consultations on the Code of Conduct in the South China Sea, strengthened practical cooperation on maritime security, promoted the construction of regional security mechanisms, and strived to make the South China Sea a sea of peace, friendship and cooperation.
Actively provide international public safety products.
China actively supports UN peacekeeping operations, is one of the major contributors to UN peacekeeping operations, and is the largest troop contributor among the permanent members of the Security Council. By December 2018, China’s army had participated in 24 UN peacekeeping operations, dispatched more than 39,000 peacekeeping military personnel, and 13 China soldiers died in the front line of peacekeeping. China’s army built and repaired more than 13,000 kilometers of roads in the peacekeeping mission area, and cleared 10,342 mines and various unexploded ordnance; Delivered more than 1.35 million tons of materials, with a total transportation mileage of more than 13 million kilometers; More than 170,000 patients were admitted; Completed more than 300 tasks such as armed guards and long-distance and short-distance patrols.
In September 2015, China joined the new standby mechanism of United Nations peacekeeping capacity, and built an 8,000-person peacekeeping standby force. In September 2017, China completed the first-level standby registration of peacekeeping standby forces in the United Nations. In October 2018, all the 13 first-level standby units passed the assessment and evaluation organized by the United Nations and were promoted to the second-level standby state. In February 2019, the United Nations upgraded five of the above-mentioned 13 second-level standby units to the third-level standby state. China actively trains peacekeepers for various countries, and has trained more than 1,500 peacekeepers for dozens of countries. In December 2018, 2,506 officers and men from China performed their duties in seven United Nations mission areas and the United Nations Department of Peacekeeping Operations.
According to the relevant resolutions of the UN Security Council, the government of China sent naval vessels to the Gulf of Aden and Somali waters to carry out regular escort operations in December 2008, and cooperated with multinational escort forces to jointly safeguard the safety of international sea lanes. In the past 10 years, China Navy has normally deployed three or four ships to carry out escort missions, sending 31 batches of more than 100 sub-ships and more than 26,000 officers and men, providing safety protection for more than 6,600 Chinese and foreign ships, and rescuing, taking care of and rescuing more than 70 ships in distress.
China’s armed forces actively participated in international disaster relief and humanitarian assistance, sent professional rescue forces to disaster-stricken countries to rescue and reduce disasters, provided relief materials and medical assistance, and strengthened international exchanges in rescue and reduction. Since 2012, we have organized or participated in the search and rescue of Malaysia Airlines flight MH370, typhoon Haiyan rescue in the Philippines, fighting against Ebola epidemic in West Africa, water shortage rescue in Maldives, earthquake relief in Nepal, and dam-break rescue in Laos. China Navy’s hospital ship "Square Boat" has been in service for 10 years, and has carried out seven "harmonious missions", visiting 43 countries in total, providing medical services and organizing medical exchanges for people in visiting countries, benefiting more than 230,000 people.
China has actively carried out international and regional anti-terrorism cooperation. Strengthen international anti-terrorism cooperation within the framework of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, organize joint anti-terrorism exercises, crack down on illegal trafficking in weapons, ammunition and explosives, cooperate to identify and cut off personnel infiltration channels, and promote international anti-terrorism information exchange and sharing. Hosting the Great Wall International Forum with the theme of counter-terrorism, and actively participating in multilateral counter-terrorism mechanisms such as the APEC Counter-Terrorism Working Group and the Global Counter-Terrorism Forum. Hold bilateral anti-terrorism consultations with relevant countries. We will promote the establishment of a coordination mechanism for anti-terrorism cooperation among the armed forces of Afghanistan, China, Pakistan and Tajikistan, hold two meetings of senior military leaders, carry out anti-terrorism exchanges and cooperation, and actively safeguard regional security.
Concluding remarks
Peace is the common aspiration of people of all countries, and development is the eternal theme of human society. In the face of increasingly complex global security challenges and the choice of where human development should go at the crossroads, China firmly believes that hegemony and expansion will eventually fail, and security and prosperity should be shared. China will stick to the path of peaceful development and work with people of other countries to safeguard world peace and promote common development.
China’s national defense in the new era, under the guidance of the supreme leader’s thought of strengthening the army, will March forward courageously towards the grand goal of building a world-class army in an all-round way along the road of strengthening the army with China characteristics. China’s army has the determination, confidence and ability to overcome all threats and challenges, provide strong strategic support for realizing the Chinese dream of the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation, and make new and greater contributions to serving and building a community of human destiny.